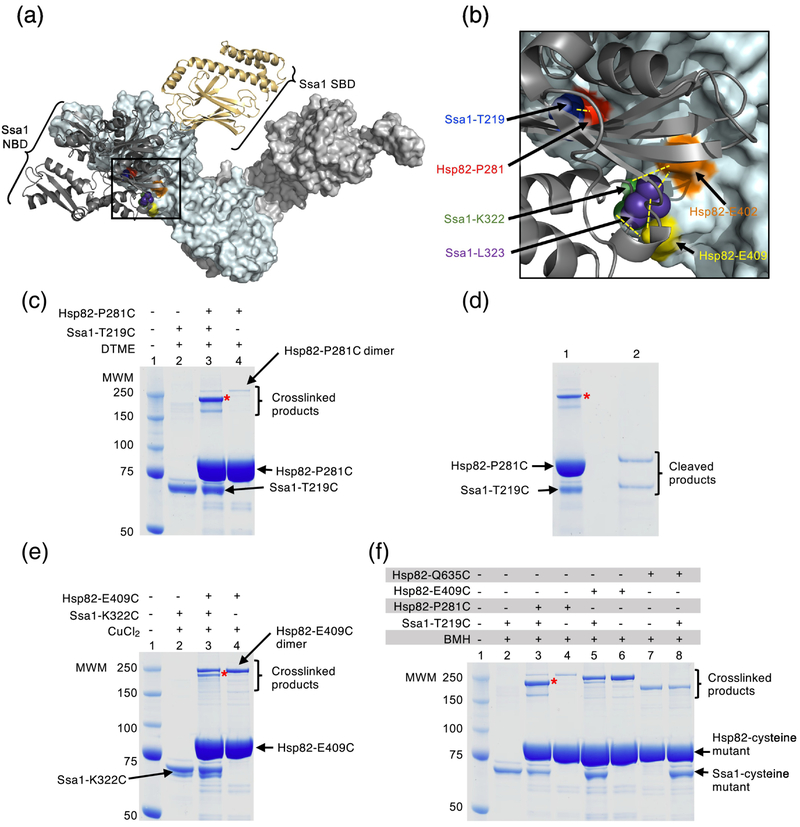
Fig. 4.
Hsp82 and Ssa1 residues directly interact. (a) Docked homology models of apo yeast Hsp82 and ADP-bound Ssa1 [33]. The apo conformation of the Hsp82 dimer is shown as a surface rendered model in light cyan and light gray and the ADP-bound conformation of Ssa1 is shown as a ribbon model with the NBD in dark gray and the SBD in wheat. Residues in Hsp82, P281, E402 and E409, that were mutated in this study are shown in red, orange and yellow, respectively, while residues in Ssa1, T219, K322 and L323, that were mutated in this study are shown as CPK models in blue, green and purple, respectively. The black square represents the field that is enlarged in (b). (b) Enlargement of the interaction region between Hsp82 and Ssa1 shown in (a). Hsp82 and Ssa1 are colored as in (a) and residues mutated in this study are also as described in (a). Yellow dashed lines indicate the pairs of Hsp82 and Ssa1 residues that were used for crosslinking experiments. (a) and (b) were both rendered using PyMOL (https://pymol.org/2/). (c) Hsp82-P281C and Ssa1-T219C (4 μM each) were treated with the crosslinker DTME (13.3 Å linker) alone and in a mixture together and covalent bond formation was monitored by SDS-PAGE followed by Coomassie blue staining. The major crosslinked species (*) is consistent with crosslinked Hsp82-P281C and Ssa1-T219C (lane 3). A small amount of a slowly migrating species was likely the covalently linked Hsp82-P281C dimer, since it was observed in reactions with and without Ssa1 (lanes 3 and 4). The minor species seen in crosslinking reactions with Hsp82-P281C and Ssa1-T219C that migrated slightly faster than the predominant species was not characterized (lane 3). (d) The predominant crosslinked species (*) from (c) lane 3 was extracted and treated with a reducing agent and the products analyzed by SDS-PAGE followed by Coomassie blue staining. (e) Hsp82-E409C and Ssa1-K322C (4 μM each) were treated with CuCl2 (~2 Å linker) alone and in a mixture together and covalent bond formation was monitored by SDS-PAGE followed by Coomassie blue staining. The Hsp82-P281C and Ssa1-T219C crosslinked species is indicated (*, lane 3) and a second species consistent with the covalently linked Hsp82-P281C dimer, since it was observed in reactions with and without Ssa1, was also observed. (f) Hsp82 mutants including Hsp82-P281C, E409C and Q635C (4 μM), and Ssa1-T219C (4 μM) are treated with BMH (13 Å linker) alone and in mixtures together as indicated and covalent bond formation is monitored by SDS-PAGE followed by Coomassie blue staining. Crosslinked dimers of Hsp82-P281C (lane 3 and 4), E409C (lane 5 and 6) and Q635C (lane 7 and 8) can be observed; Hsp82-Q635C runs at a lower molecular weight than other crosslinked products likely due to it attaining a more compact conformation following crosslinking. In (c-f), (*) indicates crosslinked product of interest and the gels shown are representative of at least three independent experiments.