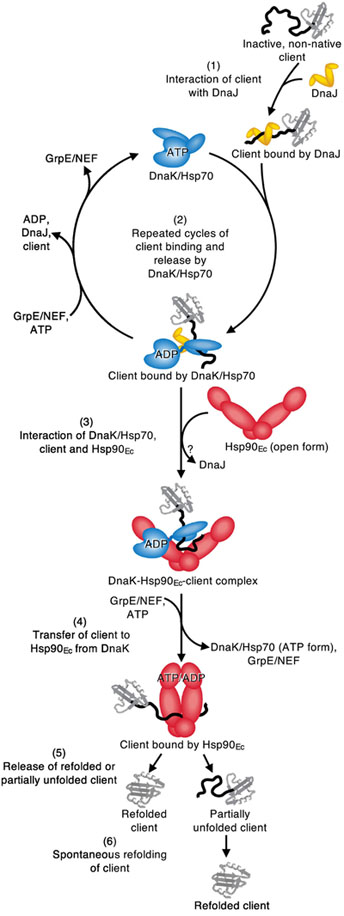
Fig. 7.
Working model for the collaboration of bacterial Hsp70 and Hsp90 in protein remodeling and activation. (1) The J-protein, DnaJ in E. coli, engages inactive, non-native client. (2) DnaK/Hsp70 is recruited to the client by DnaJ/J-protein and through rounds of client binding and release prevents client misfolding or initiates protein remodeling. (3) DnaK/Hsp70 in the ADP-bound conformation stably interacts with substrate and Hsp90 is recruited via the interaction between the DnaK/Hsp70 J-protein binding site and the M-domain of Hsp90. (4) Nucleotide induced conformational changes likely in both chaperones promote client transfer from DnaK/Hsp70 to Hsp90. (5) Client is released from Hsp90 in either a partially remodeled state or in an active conformation. (6) Spontaneous refolding of partially remodeled client can occur. See Results for details of the model.