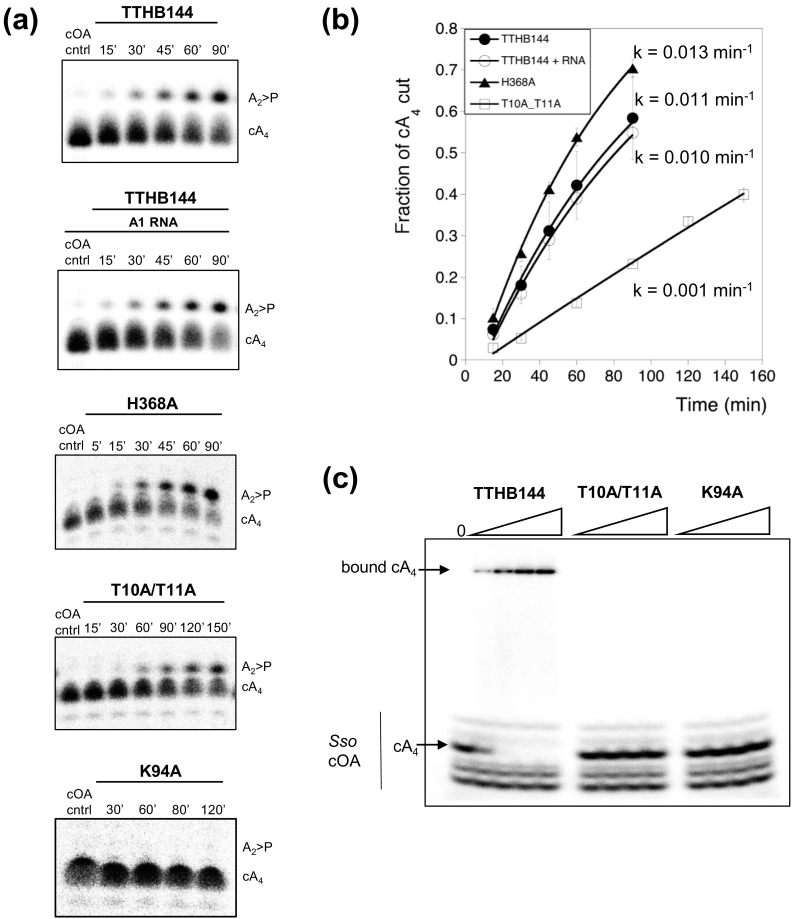
Fig. 3.
cA4 binding and cleavage by wild-type and variant TTHB144 enzymes. (a) Panels are phosphorimages of denaturing PAGE visualizing degradation of 200 nM radiolabeled cA4 by TTHB144 and variants (8 μM dimer) at 70 °C. cA4 is degraded to A2 > P. Time in minutes is indicated. Protein and radiolabeled cA4 were incubated in pH 8.0 buffer containing 20 mM Tris–HCl, 150 mM NaCl, 1 mM EDTA and 3 units SUPERase•In™ inhibitor, and reactions were quenched at the indicated time-points by phenol–chloroform extraction. A cA4 degradation assay was also carried out in the presence of 1 μM A1 RNA in order to evaluate the effect of RNA binding and cleavage at the HEPN active site on cA4 degradation at the CARF domain. (b) Plot of the fraction of cA4 cut versus time, generated by quantifying the densiometric signals from the phosphorimages depicted in panel a. All data points are the average of at least three technical replicates and are fitted to an exponential rise equation to derive the rate of cA4 degradation, as described previously [21]. Data points for TTHB144 are the average of six replicates encompassing two biological replicates with three technical replicates for each. Error bars show the standard deviation of the mean. (c) Electrophoretic mobility shift assay of radioactively-labeled cOA generated by the S. solfataricus Csm complex. cA4 is indicated; minor bands correspond to linear and cyclic byproducts of the reaction. cA4 (20 nM) was incubated with TTHB144 or variants T10A/T11A or K94A (0.1, 1, 10 or 20 μM protein dimer) in buffer containing 20 mM Tris–HCl (pH 7.5), 150 mM NaCl and 2 mM MgCl2 supplemented with 2 μM Ultrapure Bovine Serum Albumin (Invitrogen) for 10 min at 25 °C. A reaction volume equivalent of 20% (v/v) glycerol was then added prior to loading the samples on a 15% polyacrylamide, 1 × TBE gel. Electrophoresis was carried out at 25 °C and 200 V.