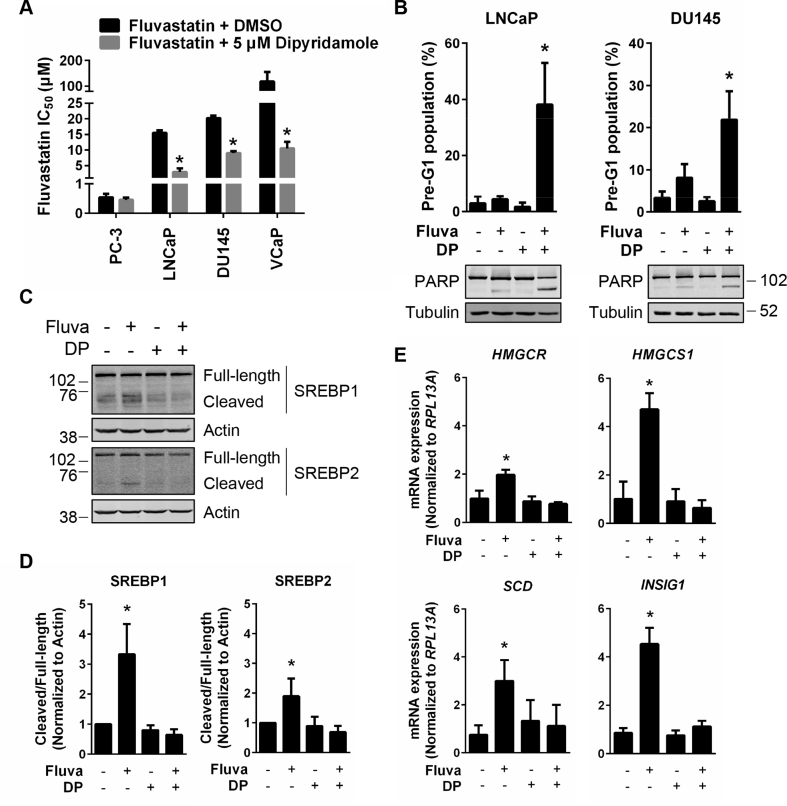
Figure 5.
Dipyridamole inhibits fluvastatin-induced SREBP activation and potentiates fluvastatin-induced apoptosis in PCa cell lines. (A) PCa cell lines were treated with a range of fluvastatin doses ± a sub-lethal dose (5 μM) of dipyridamole for 72 h, and cell viability was determined using an MTT assay. The IC50 values are plotted. Error bars represent the mean + SD, n = 3–5, *p < 0.05 (Student t test, unpaired, two-tailed). (B) LNCaP and DU145 cells were treated with solvent controls, 10 μM fluvastatin, 5 μM dipyridamole (DP) or the combination for 72 h, fixed in ethanol and assayed for DNA fragmentation (% pre-G1 population) as a marker of cell death by propidium iodide staining. Error bars represent the mean + SD, n = 3, *p < 0.05 (one-way ANOVA with Tukey's multiple comparisons test). Protein was also isolated from cells after 72 h of treatment and immunoblotting was performed to assay for PARP cleavage. (C) LNCaP cells were treated with 10 μM fluvastatin ±5 μM DP for 8 h, and protein was isolated to assay for SREBP1 and SREBP2 expression and cleavage (activation) by immunoblotting. (D) SREBP1 and SREBP2 cleavage (cleaved/full-length) was quantified by densitometry and normalized to Actin expression. Error bars represent the mean + SD, n = 3, *p < 0.05 (one-way ANOVA with Bonferroni's multiple comparisons test, where each group was compared to the solvent controls group). (E) LNCaP cells were treated with 10 μM fluvastatin ±5 μM DP for 16 h, and RNA was isolated to assay for HMGCR, HMGCS1, INSIG1 and SCD expression by qRT-PCR. mRNA expression data are normalized to RPL13A expression. Error bars represent the mean + SD, n = 3, *p < 0.05 (one-way ANOVA with Bonferroni's multiple comparisons test, where each group was compared to the solvent controls group).