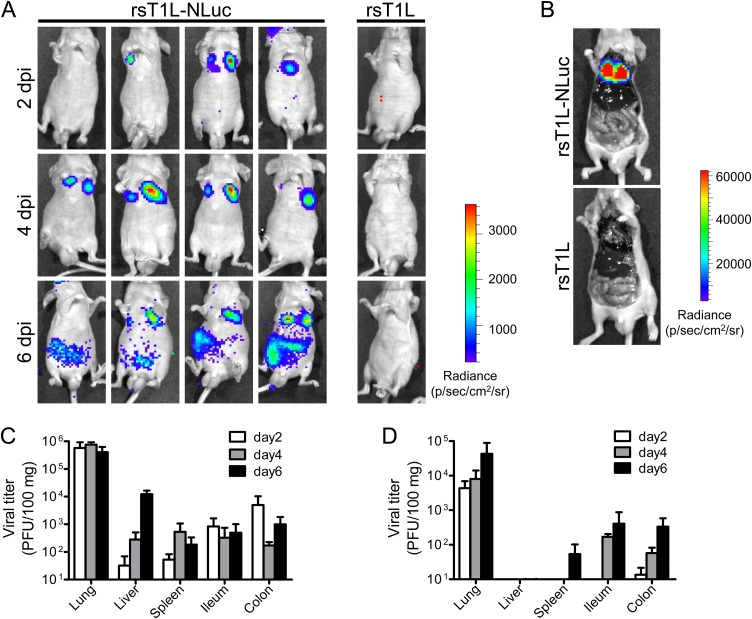
FIG 2.
Live luminescence imaging of rsT1L-NLuc virus infection in mice. (A to D) BALB/c nude mice were infected intranasally with 1.4 × 107 PFU of rsT1L or rsT1L-NLuc. At 2, 4, or 6 days postinfection (dpi), NLuc substrates were injected via the retro-orbital venous sinus and the bioluminescence signal was obtained using an in vivo imaging system (IVIS). (B) At 4 dpi, animals were sacrificed after inoculation of NLuc substrate and the body cavities were opened. Carcasses were subjected to IVIS observation. (C and D) At 2, 4, or 6 dpi, animals were sacrificed after IVIS observation and infectious virus titers in tissue homogenates were examined. (C) rsT1L; (D) rsT1L-NLuc. Data are expressed as the mean ± standard deviation (SD) (n = 4).