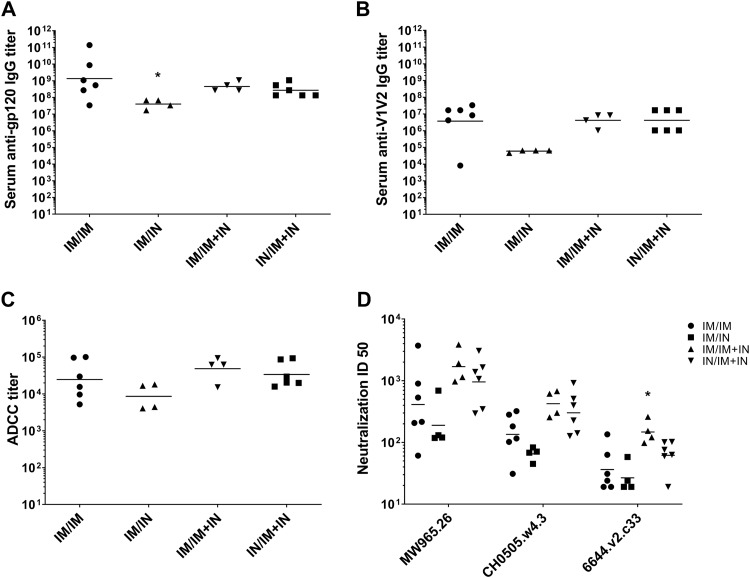
FIG 5.
Combined intramuscular and intranasal boosting, regardless of intramuscular or intranasal prime, induces serum anti-HIV antibodies similar to those induced by an intramuscular prime/boost regimen in rabbits. New Zealand White rabbits (n = 4 to 6/group) were primed i.m. or i.n. with MVAgp120 in week 0 and boosted with 100 μg gp120 adjuvanted with AddaVax i.m. and/or with 435 μg gp120-Ad2F adjuvanted with 64 μg M7 i.n. in weeks 12 and 16. Serum antibody titers and viral neutralization from blood drawn in week 19 are shown. (A) Serum gp120-specific IgG titers. Serum anti-gp120 IgG titers induced i.m./i.n. were significantly lower than serum anti-gp120 IgG titers induced i.m./i.m (P = 0.01). (B) Serum V1V2-specific IgG titers were not significantly different between groups. A Kruskal-Wallis test result was not significant (P = 0.057), so multiple comparisons were not made. (C) ADCC activity using human effector cells against HIV gp120-coated target cells. There were no significant differences between groups (P = 0.19). (D) Neutralization of tier 1a (MW965.26 and CH0505.w4.3) and tier 1b (6644.v2.c33) pseudoviruses. I.m./i.m.-plus-i.n. immunization induced significantly greater neutralization of 6644.v2.c33 (P = 0.04) than immunization by the i.m./i.m. route. The horizontal lines indicate the geometric mean titers.