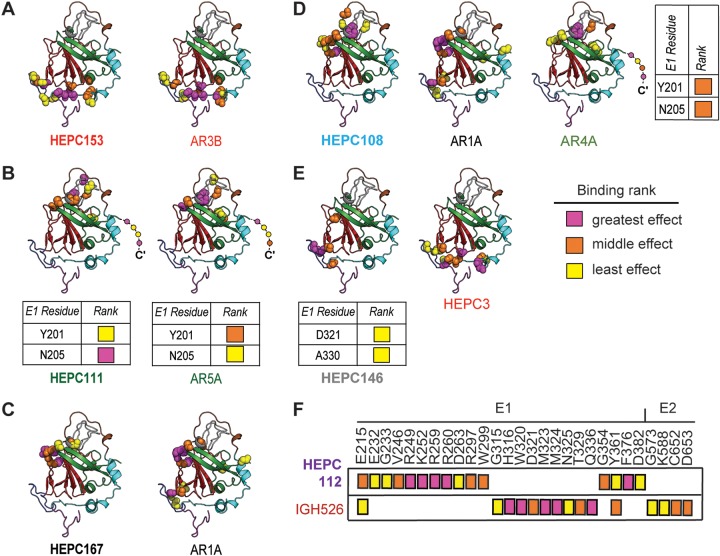
FIG 4.
Mapping of probable binding residues of each MAb onto the E2 ectodomain crystal structure. One C18 MAb representative of each antigenic cluster in Fig. 2 is shown, with the reference MAb or MAbs with which is shares the most probable binding residues, namely, (A) HEPC153, (B) HEPC111, (C) HEPC167, (D) HEPC108, (E) HEPC146, and (F) HEPC112. For each MAb, up to 15 probable E2-binding residues are shown, marked with colored spheres on the HCV E2 structure (Flyak et al., PDB 6MEI) (34). Probable E1-binding residues are shown in tabular form. These 15 E1E2 binding residues were also subdivided into tertiles of greatest effect (magenta), middle effect (orange), and least effect (yellow) of mutation to alanine on MAb binding. E2 structural components were highlighted in PyMOL, including the AS412 site (purple), front layer (cyan), VR2 (brown), CD81 binding loop (blue), beta sandwich (red), VR3 and post-VR3 (gray), and back layer (green). Dashed line indicates the stalk region of E2 not present in the ectodomain structure. MAb names are color-coded according to hierarchical clustering in Fig. 2.