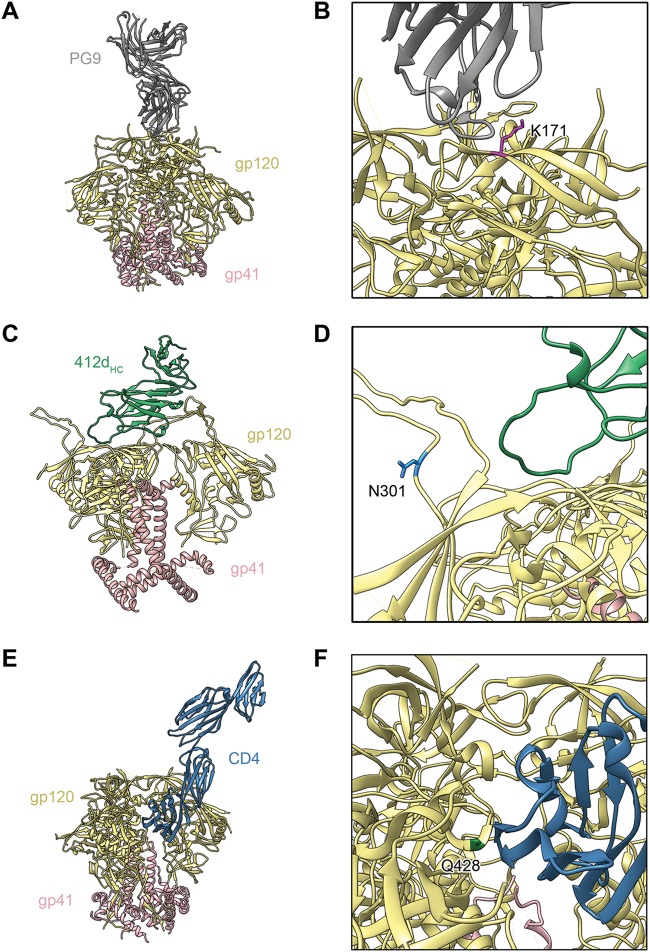
FIG 7.
Modeling of Env trimers, highlighting some of the eCD4-Ig selected mutated residues. (A) Model of apex V2 glycan bNAb PG9 in complex with the BG505 SOSIP.664 trimer (PDB accession no. 5VJ6) (67). gp120 is depicted in tan, gp41 in pink, and PG9 in gray. (B) Detailed view of the structure in panel A. Apex residue K171, which is altered to glutamic acid in some eCD4-Ig-selected Env variants, is highlighted in magenta. (C) Model of CD4-induced bNAb 412d heavy chain (412dHC) in complex with an Env trimer in a partially open conformation, created by combining the crystal structure of BG505 SOSIP gp140 with that of 412d complexed with HIV-1 YU2 gp120 (PDB accession no. 4NCO and accession no. 2QAD) (68, 69). 412dHC is depicted in green. (D) Detailed view of the structure in panel C. Residue N301, which is altered to aspartic acid in some eCD4-Ig-selected Env variants, is shown in light blue. (E) Model of the BG505 DS-SOSIP trimer in complex with CD4 (PDB accession no. 5U1F) (70). CD4 is depicted in dark blue. (F) Detailed view of the structure in panel E. CD4-binding site residue Q428, which is altered to lysine or arginine in some eCD4-Ig-selected Env variants, is highlighted in green.