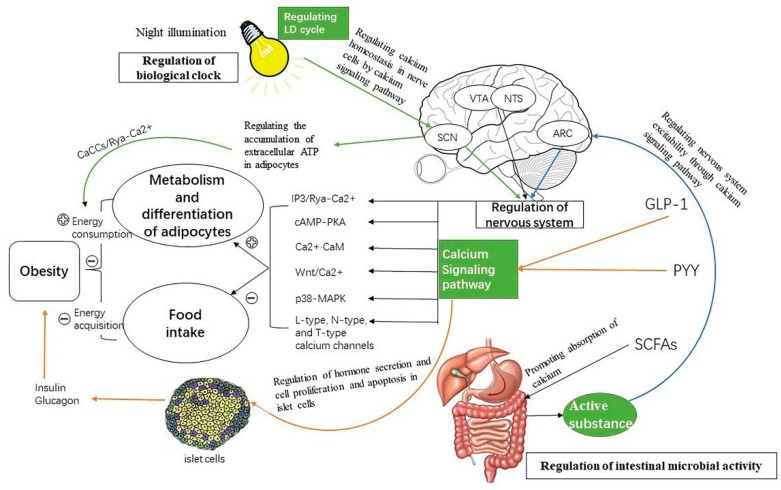
Figure 2.
The description of the mechanisms by which the nervous system, the gut microbes, and the circadian rhythms regulate obesity through calcium signaling. This paper summarizes the diagrams of nervous system, light rhythm, and intestinal microorganisms regulating energy consumption and acquisition through calcium signaling pathways. Light changes the activity of SCN neurons by activating calcium signaling pathways, and these signals are transmitted through neurons to brain regions associated with food intake to enhance satiety and inhibit food intake. On the other hand, a signal is transmitted to adipocytes by light, which can promote adipocyte metabolism and heat production by activating DAG-IP3 and cAMP-PKA pathways to increase energy consumption. GLP-1, PYY, and SCFAs secreted by intestinal microorganisms act on the PVN region of the brain, activating feeding-related neurons to enhance satiety and inhibit feeding. IP3-DAG and RTK-Ras-raf-MEK-ERK pathways act on adipocytes to regulate adipocyte metabolism and promote lipid decomposition [25,26]. Directly acting on pancreatic tissue: the proliferation of islet B cells is promoted by many calcium signaling pathways, such as the PLC (phospholipase C)-ERK1/2 and the PKC pathways, and the apoptosis of islet B cells is inhibited by the IP3-DAG and the MAPK pathways to ensure that the pancreatic tissue meets the needs of insulin, which may be related to obesity. Signals regulate insulin secretion through the cAMP and the PKA-Syt7 pathways, which are positively or negatively correlated with obesity. Signaling molecule Nesfatin-1 acts on neurons of VTA (ventral tegmental area) and NTS through N-type and T-type calcium channels, enhancing satiety and inhibiting feeding [55,60,61,62,63,64]. Signals are transmitted to adipocytes when there is sympathetic excitation, and the metabolic heat production of brown adipocytes is regulated by cAMP-PKA, TRPV1, TRPA1, and -IP3-DAG pathways to increase energy consumption [83,92,93,94].