Fig. 3.
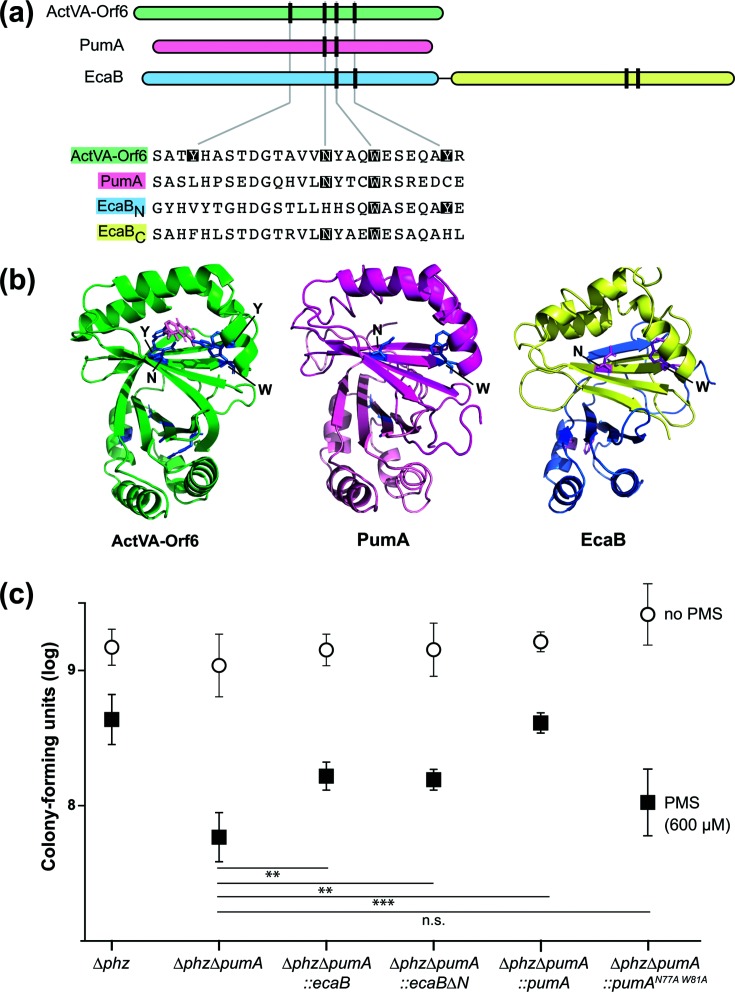
PumA shows homology to the S. coelicolor monooxygenase ActVA-Orf6 and the S. coelicolor protein EcaB, which also confers PMS tolerance in P. aeruginosa. (a) Top: domain architectures of the S. coelicolor monooxygenase ActVa-Orf6, P. aeruginosa PumA and the S. coelicolor SoxR-target EcaB. Vertical lines represent the locations of residues that are important for ActVA-Orf6 activity. Bottom: alignment of selected regions from S. coelicolor ActVA-Orf6, P. aeruginosa PumA and S. coelicolor EcaB. Catalytic site residues identified in S. coelicolor ActVA-Orf6 that are conserved are indicated with shading. (b) Structure of S. coelicolor ActVA-Orf6 (left), and threaded structures of P. aeruginosa PumA (middle) and S. coelicolor EcaB (right). The domains are colour-coded as in panel (a). (c) Assay for tolerance to 600 µM PMS. Biofilms were grown on 1 % tryptone+1 % agar for 4 days, and then whole colonies were homogenized for colony-forming unit plating. The error bars represent the standard deviation of biological quadruplicates. P-values were calculated using unpaired, two-tailed t-tests (P>0.05 was considered not significant; **P≤0.005; ***P≤0.0005).