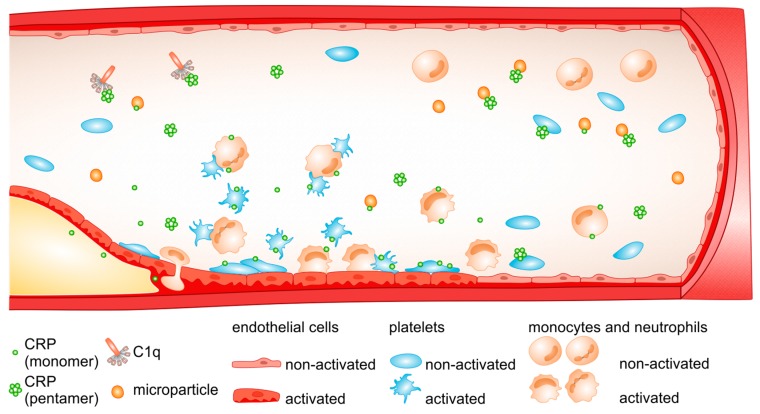
Figure 1.
Possible interactions of CRP with blood cells and plasma components. Pentameric CRP (nCRP) bound to microbial polysaccharides or ligands exposed on damaged cells activates the classical complement pathway through the interaction with C1q. Both pro-and anti-inflammatory effects are attributed to nCRP via its interactions with blood cells (for details, please see Section 3). At the site of the injured endothelium, circulating platelets undergo activation and spread. On the surface of the activated platelets, circulating cell-derived microparticles and apoptotic cell membranes, pentameric CRP dissociates to monomeric CRP (mCRP), which exerts pro-inflammatory effects by activating blood cells and by promoting inflammatory response. mCRP can be deposited in atherosclerotic lesions.