Figure 1.
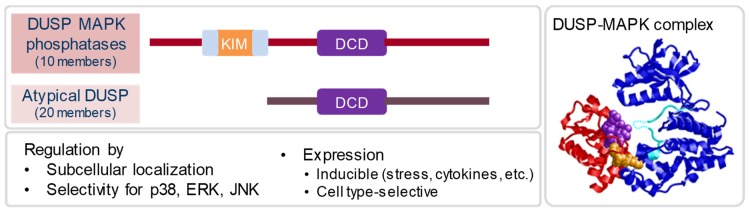
Dual-specificity phosphatases (DUSP): domain structure, mode of action, and levels of regulation. The 10 members of the classical DUSP-MAPK phosphatases contain a MAPK-binding kinase-interaction motif (KIM) conferring selective binding to ERK1/2, p38 or JNK1/2. Upon binding to MAPK, the DUSP catalytic domain (DCD) dephosphorylates the TXY motif in the activation loop (right panel). Atypical DUSPs lack a KIM and can have more diverse substrates, including phosphorylated RNA (DUSP11). Regulated expression between cell types and after stimulation, different compartmentalization of DUSP, and selectivity in binding to MAPK family members confers specificity of DUSP action in signaling.