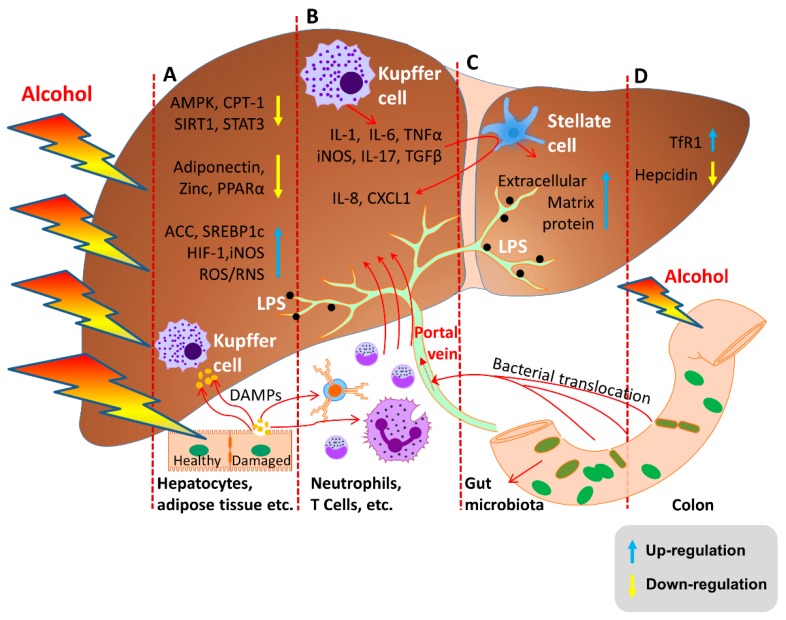
Figure 1.
Molecular mechanisms of ALD. (A) Alcohol and its metabolites cause AFL by increasing ROS/RNS levels and the expression of ACC and SREBP1c. Additionally, via the reduced expression of AMPK-SIRT1, adiponectin, and zinc which activate PPARα. (B,C) Excessive alcohol consumption-enhanced permeability of the colon allows LPS to enter into the liver through the portal vein. The activated Kupffer cells release cytokines such as IL-1, IL-17, TGF-β, iNOS, and TNF-α which activates stellate cells and release IL-8 and CXCL1 in AH and ASH. Activated stellate cells also release the extracellular matrix which results in liver fibrosis. (D) Regulation of hepcidin, one of the main pathogenic factors in ALD.