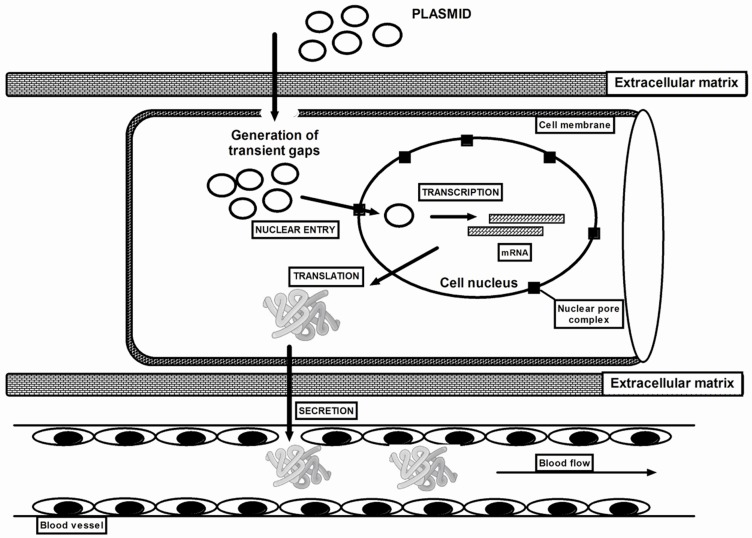
Figure 1.
Schematic diagram of proposed plasmid DNA delivery with the use of electroporation. Plasmid DNA (pDNA) must overcome barriers, including extracellular matrix, cell membrane, cytoplasm and nuclear membrane before reaching the nucleus. However, applying an electric current with an appropriate voltage facilitate the transport of pDNA through biological membranes. Plasmids penetrate into the target cell cytoplasm through the transiently formed gaps in the sarcolemma. DNA in the cytoplasm is exposed to degradation by cytoplasmic nucleases. Finally, the DNA through nuclear pore complexes has to penetrate the nuclear membrane to enter the nucleus where the transcription occurs. The delivered plasmid DNA may silence genes or be transcribed into the missing protein and then secreted into the bloodstream.