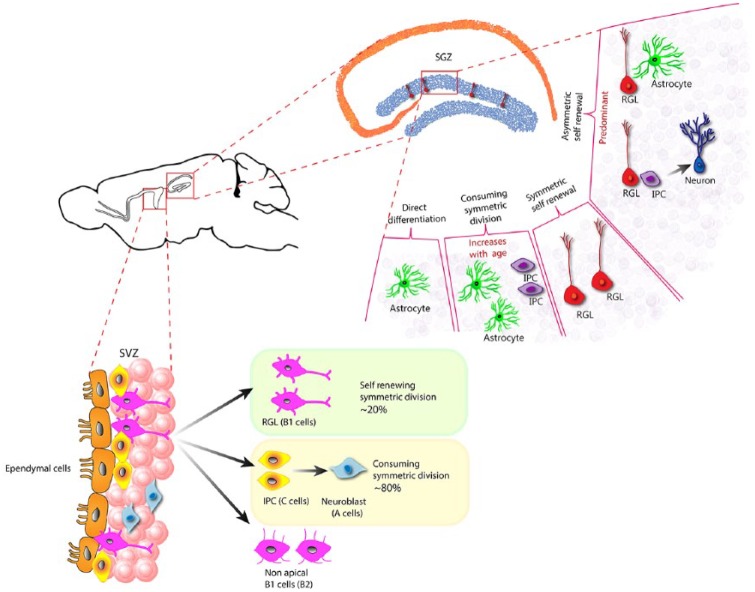
Figure 5.
Fate potential of adult neural stem cells in SGZ and SVZ.
The quiescent radial glial-like (RGL) cells, in the SGZ upon activation can undergo four distinct routes: they can asymetrically divide to self-renew and make an astrocyte or an intermediate proliferating cell (IPC). An RGL can also undergo symmetric division to make two RGLs resulting in only self-renewal without making a differentiated progeny. An RGL could also undergo consuming symmetric division making two astrocytes or two IPC, without self-renewing itself, and finally, an RGL could undergo direct differentiation without cell division to become an astrocyte. The mode of asymmetric self-renewing division is the more common outcome in an adult healthy brain, whereas the consuming symmetric division is thought to increase with age, resulting in reduction in NSC in aged brains. In the SVZ, the RGL mostly undergo symmetric cell division that could be either self-renewing or consuming. The SVZ RGL symmetric self-renewal could occasionally also result in another type of RGL that lack the apical process, named as the non-apical B1 cells or B2 cells.