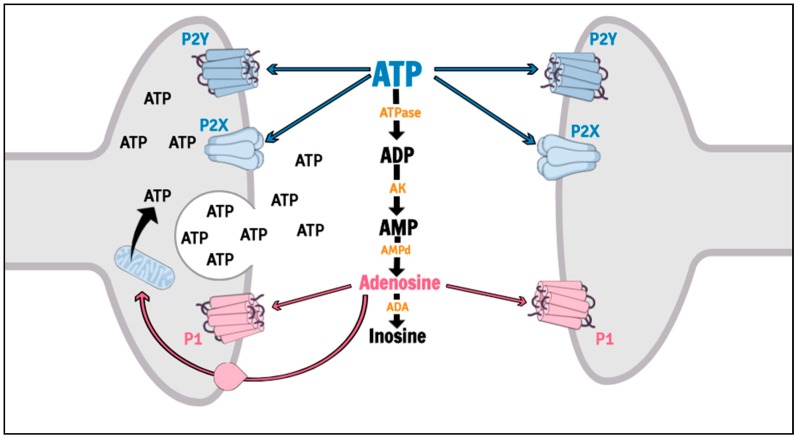
Figure 2.
Purinergic signaling. ATP is synthesized in terminal nerves, glial cells or astrocytes by mitochondrial oxidative phosphorylation, and released to extracellular space after physiological or pathological stimulus by vesicular exocytosis, transmembrane channels (pannexin, connexin) or cellular apoptosis. Extracellular ATP may either interact with P2 receptors or be rapidly metabolized to adenosine. P2 receptors are divided in P2X (cation ionotropic) and P2Y (metabotropic) receptors. Adenosine molecules may interact with P1 receptors (metabotropic), they can be reuptaken and converted back into ATP in cell cytoplasm or they can be metabolized by ADA into inosine. ATP: adenosine triphosphate; ATPase: adenosine triphosphatase; AK: adenylate kinase; AMPd: adenosine monophosphate deaminase; ADA: adenosine deaminase.