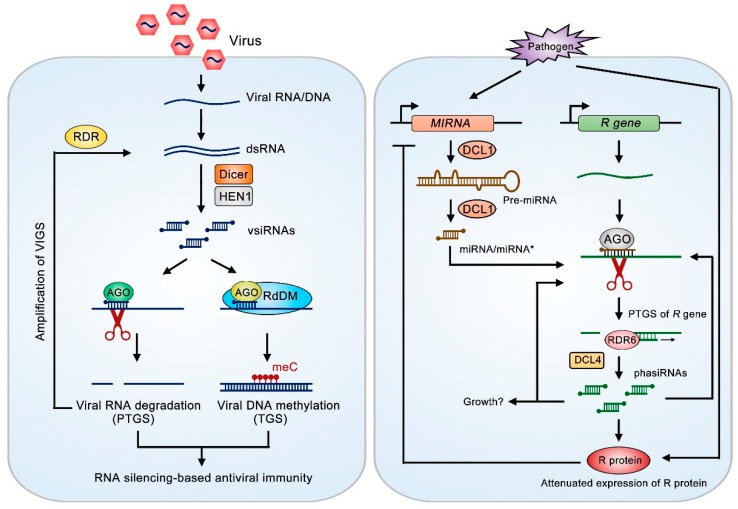
Figure 1.
RNA silencing-based immunity and its cross-talk with R gene-mediated immunity. Left panel: RNA silencing-based immunity. Replication of viral RNA triggers the synthesis of dsRNAs, which are then processed by Dicer RNase into 21–24 nt siRNAs. Some 21–22 nt vsiRNAs are loaded onto Argonaute-RNA-induced silencing complex (AGO-RISC) complex (such as AGO1 in Arabidopsis) to mediate sequence-specific degradation of viral RNAs (PTGS). Virus-induced gene silencing (VIGS) can be amplified by RDR-dependent formation of dsRNA from the cleaved target mRNA. 24 nt vsiRNAs are loaded onto AGO-RdDM silencing complex to target viral DNA for DNA methylation modification, thereby leading to silencing of viral genes at TGS level. Some pathogens are capable of interfering with miRNA biogenesis to facilitate infection. Right panel: In plants, miRNA is firstly transcribed from MIRNA gene by pol II and processed into pre-miRNA, the stem loop precursor, and then processed into miRNA/miRNA* duplex by DCL1. Mature miRNA is loaded into AGO-RISC complex to trigger degradation of R gene mRNA, leading to attenuated expression of R protein. Some R gene-targeting miRNAs is capable of triggering the production of RDR6 and DCL3-dependent phased secondary siRNA (phasiRNAs) from the cleavage site of R gene mRNA. The R gene-derived phasiRNA can induce trans-acting silencing of R gene or other target genes (such as growth-related gene). In addition, perception of pathogen infection will activate the expression of R genes, and R protein can also exert a negative regulation on the expression of MIRNA gene.