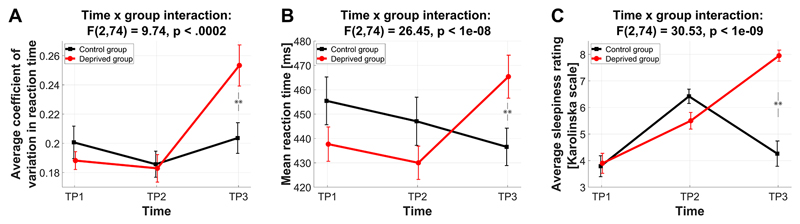
Figure 1. Sleep deprivation results in higher reaction time variability and increased reaction times.
TP1: first morning, TP2: evening, TP3: second morning. (A) Coefficient of variation in reaction time. (B) Mean reaction times (C) Self-reported subjective sleepiness obtained from the Karolinska Sleepiness Scale (Akerstedt and Gillberg, 1990).