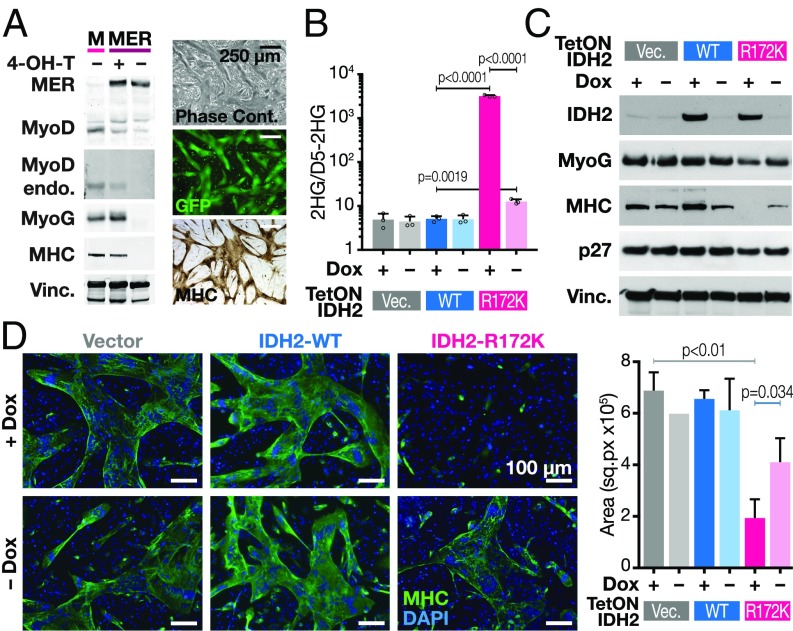
Fig. 1.
2HG-producing IDH2 mutations block the ability of MyoD to drive myotube differentiation. (A) 10T1/2 cells were transduced with wild-type MyoD (M) or MyoD-ER (MER) fusion cDNA-encoding lentiviral vectors and grown in the presence or absence of 4-OH-T. Western blots were probed with indicated antibodies (Top shows exogenous MyoD-ER and endogenous MyoD; second blot shows only endogenous MyoD; MyoG, myogenin; MHC, myosin heavy chain; Vinc, vinculin). Right are representative images of myotubes by phase contrast microscopy (Top), GFP (Middle), and immunohistochemistry for MHC (Bottom). (B) 10T1/2 cells were transduced with constructs containing doxycycline inducible (Tet-ON) vector, IDH2-WT, or IDH2-R172K in the presence or absence of doxycycline. 2HG levels shown were measured by GCMS and normalized to spiked-in D5-2HG. Data are mean ± SD of three biological replicates. P values were determined using unpaired Student’s t test. (C) Western blot of 10T1/2 cells transduced with doxycycline-inducible constructs as indicated in B. (D) Fluorescence microscopy of cells as described in C. MHC is in green; DAPI is in blue. Quantification of MHC stained areas is shown on Right. Data are mean ± SD of MHC signal from three representative areas. P values were determined using unpaired Student’s t test.