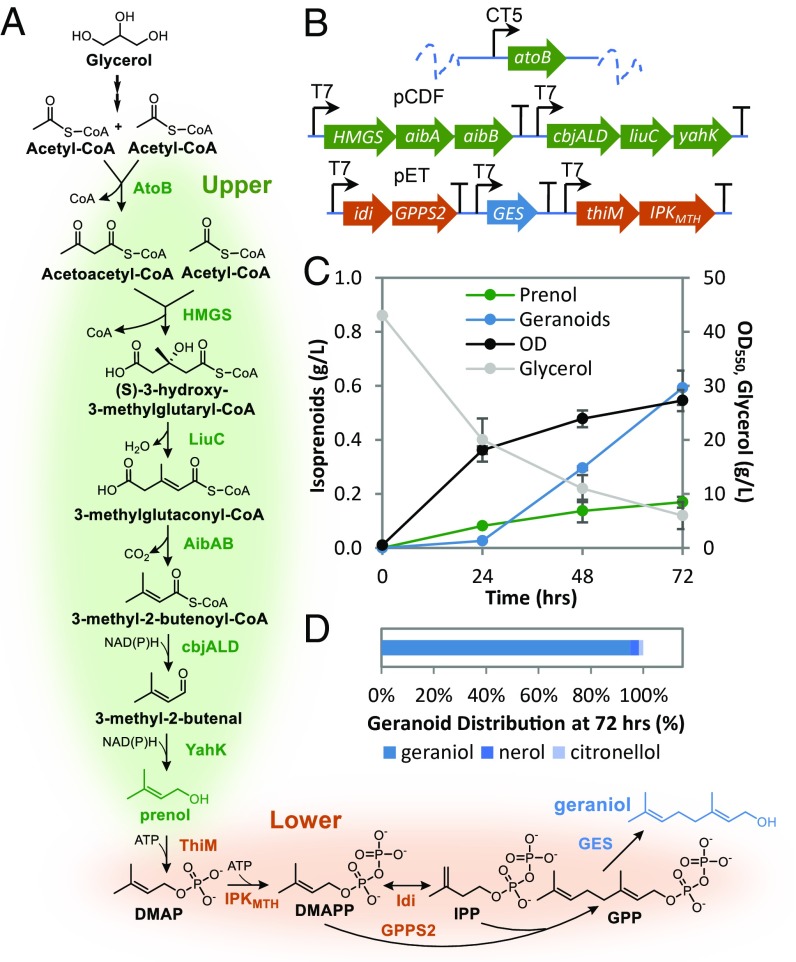
Fig. 4.
Isoprenoid production from a single nonrelated carbon source (glycerol) through the IPA pathway. (A) Integrated IPA pathway for geraniol production. Enzymes overexpressed for various pathway steps shown. (B) Schematic of E. coli construct for geranoids production. Host strain JST06 (DE3) ΔfadB is a JC01 (DE3) derivative with additional deletions to native thioesterase genes. Chromosomal expression of E. coli native atoB was regulated by a cumate-inducible PCT5 promoter. All other enzymes were expressed from pCDF or pET plasmid as shown. (C) Monoterpenoids (blue; total of geraniol, nerol, and citronellol), prenol (green), and cell growth (gray) by JST06 (DE3) atoBCT5 ΔfadB harboring pCDF-P1-HMGS-aibA-aibB-P2-cbjALD-liuC-yahK and pET-P1-idi-trGPPS2-P2-GES-P3-ThiM-IPKMTH. The strain was grown in 5 mL LB-like MOPS medium with 40 g/L glycerol with a 15% dodecane organic in 25 mL flasks (stoppered with foam plugs) incubated at 30 °C and 200 rpm. Estimates on product loss due to volatilization described in SI Appendix, Fig. S7. (D) Distribution of monoterpenoids after 72 h.