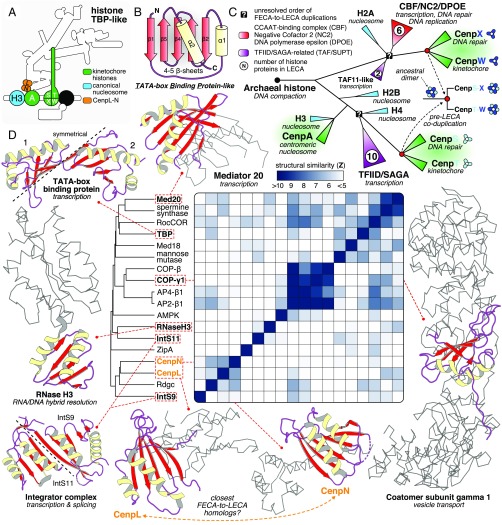
Fig. 3.
A common origin of kinetochore histones and TBP-like proteins with complexes involved in DNA repair and transcription. (A) Overview of the position of CenpA and CenpS-X-T-W (histones, green) and CenpL-N (TBP-like, orange) in the kinetochore. (B) The TBP-like fold is a set of curved β-strands that form an interaction surface for substrates (RNA/DNA, amino acid motifs) and potential dimer interfaces. (C) A cartoon of the evolutionary reconstruction of kinetochore-related histone proteins CenpA and CenpS-T-X-W (based on SI Appendix, Fig. S1I). A histone of archaeal descent duplicated and subfunctionalized many times, giving rise to a large diversity of histone proteins in eukaryotes, including those involved in the kinetochore, chromatin structure (nucleosome), transcription (TAF/SUPT/NC2/CBF), and DNA repair (DPOE). CenpA is the closest homolog of the nucleosomal histone H3. CenpS-T and CenpX-W are likely each other’s closest paralogs, signifying a coduplication of an ancient dimer to form the tetramer CenpS-X-T-W. The CenpS-X dimer also plays a role in the Fanconi anemia pathway (DNA repair). (D) Yellow (helices) and red (sheets) show the location of a TBP-like domain in a subset of available TBP-like protein structures. The gray ribbon representation indicates the nonhomologous parts of the proteins; their cellular function is indicated between brackets. CenpL and CenpN contain a TBP-like fold. Average linkage clustering of similarity scores (z-scores) indicates that CenpN and CenpL could be each other’s closest homologs.