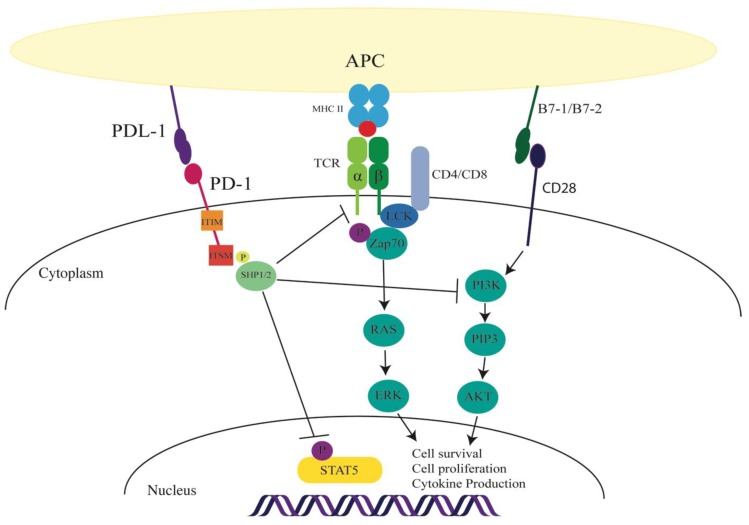
Figure 1.
Consequence of programmed cell death-1 (PD-1) activation in immune cells. On engagement of the PD-1 receptor (either through programmed death ligand (PDL) -1 or 2), the PD-1 receptor recruits Sc homology region 2 domain-containing phosphatase (SHP)1/2 to the immunoreceptor tyrosine-based switch motif (ITSM) cytoplasmic tail. PD-1 signaling can inhibit the T cell receptor (TCR) signaling cascade. In hepatitis C virus (HCV) Tregs, the signaling can inhibit signal transducer and activator of transcription 5 (STAT5) phosphorylation. PD-1 inhibition is indicated by T bars; solid arrows indicate TCR and CD28 signaling pathways.