-
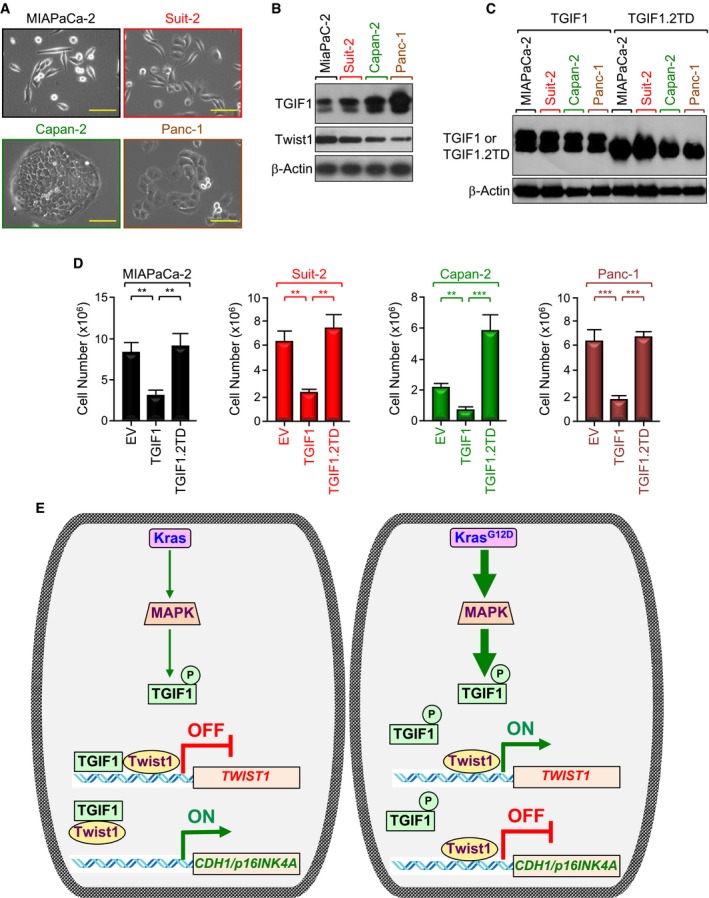
A
Representative microscope pictures (20×) of MIAPaCa‐2, Suit‐2, Capan‐2, and Panc‐1 cells. Scale bars, 200 μM.
-
B
Expression of TGIF1 and Twist1 in MIAPaCa‐2, Suit‐2, Capan‐2, and Panc‐1 cells was analyzed by immunoblotting.
-
C, D
MIAPaCa‐2, Suit‐2, Capan‐2, and Panc‐1 cells were transfected with empty vector (EV), wild‐type (TGIF1), or phosphorylation‐mimic mutant (TGIF1.2TD) of TGIF1. Cell extracts were analyzed 48 h following transfection by immunoblotting using anti‐Flag antibody (C). Cells were selected with neomycin for 2–3 weeks and counted using an automatic cell counter (D) (n = 6). Data are expressed as mean ± SEM. **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001; based on a two‐tailed Student's test.
-
E
Model of suppression of TGIF1 function by KrasG12D/MPK‐mediated phosphorylation. In this model, acquisition of KrasG12D leads to constitutive activation of MAPK/ERK, which in turn phosphorylates TGIF1. Phosphorylation of TGIF1 disrupts its ability to inhibit Twist1 expression, thereby leading to suppression of CDH1 and p16INK4A expression and attendant PDAC formation and progression.