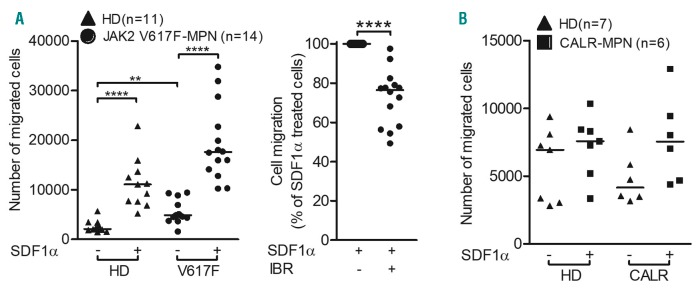
Figure 3.
Stromal cell-derived factor 1 alpha-induced chemotaxis of primary granulocytes isolated from peripheral blood of JAK2-V617F-positive patients with myeloproliferative neoplasms could be impeded by a clinically relevant dose of ibrutinib. Granulocytes were isolated (Ficoll-paque density gradient centrifugation- erythrocyte lysis based method) from peripheral blood of healthy donors (▲: HD), and patients with untreated JAK2-V617F-positive (●: JAK2 V617F-MPN) (A) or CALR-mutated (■: CALR-MPN) (B) myeloproliferative neoplasia (MPN). The protocol was approved by the local ethics committee (protocol n. MD115/08), and all patients signed informed consent. The cells were rested for 30 min in starvation medium (0.5% fetal bovine serum) and left alone (A, left panel and B) or treated with dimethylsulfoxide (DMSO) or 0.5 mM of ibrutinib (IBR) (A, right panel) for an additional 1 h and chemotaxis assays were performed (pore size: 3 mm). Starvation medium (0.5% fetal bovine serum) containing stromal cell-derived factor 1 alpha (SDF1α: 100 ng/mL) served as the chemoattractant. Chemotaxis of IBR-treated cells was normalized to that of DMSO-treated cells. The horizontal lines indicate medians and the statistical significance of differences between control and treated samples was calculated by the Mann-Whitney test; *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001 and ****P<0.0001.