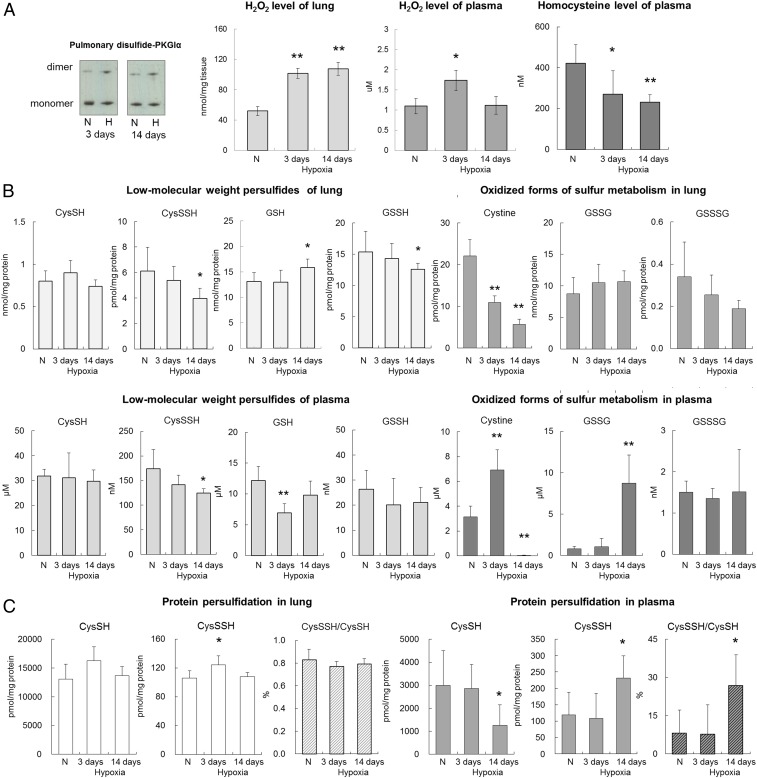
Fig. 2.
Reactive oxygen and sulfur species level in lung and plasma of mice subjected to chronic hypoxia. (A) Representative disulfide PKGIα increase in lungs of WT mice subjected to either normoxia or chronic hypoxia for 3 and 14 d. (B) Low-molecular-weight persulfides and oxidized forms of sulfur metabolism in lung and plasma of WT mice subjected to either normoxia or chronic hypoxia for 3 and 14 d. Thiol and hydropersulfide-containing compound were alkylated with tyrosine and a hydroxyphenyl-containing derivative, β-(4-hydroxyphenyl)ethyl iodoacetamide (HPE-IAM), and their HPE-IAM adducts were quantified by liquid chromatography-electrospray ionization-tandem mass spectrometry (LC-ESI-MS/MS). (C) Protein persulfidation in lung and plasma of WT mice subjected to either normoxia or chronic hypoxia for 3 and 14 d. Protein-bound hydropersulfides were alkylated with HPE-IAM, and pronase digest samples were quantitatively analyzed by LC-ESI-MS/MS. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01 versus normoxia; n = 6 to 8 per group. In some cases, the aspect ratio of the original immunoblots was altered to enable a concise multipanel figure with a consistent presentation style; the original uncropped representative images of these immunoblots are also available in SI Appendix, Fig. S10.