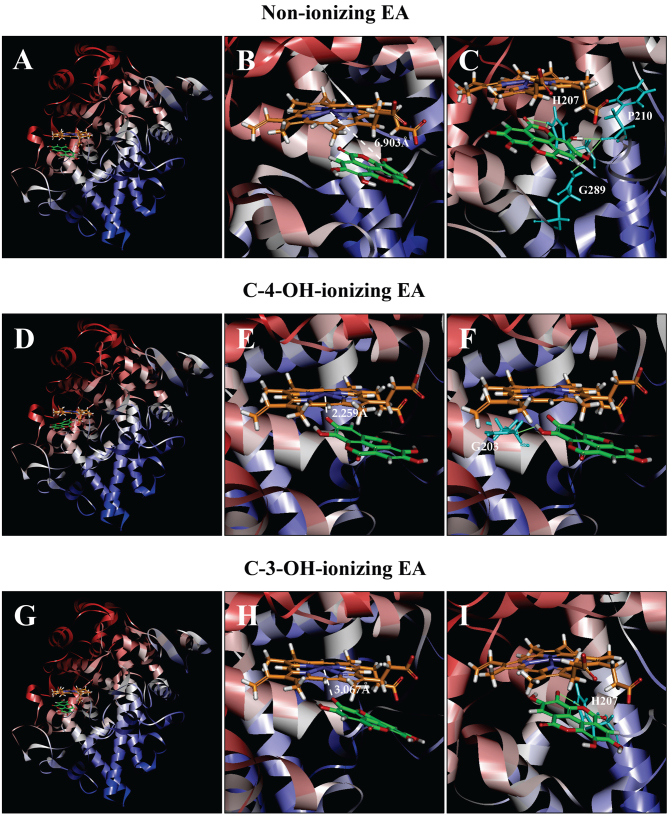
Figure 6.
Molecular docking analysis of the binding interaction of COX I with non-ionizing EA (A-C), C4-OH-ionizing EA (D-F), and C-3-OH-ionizing EA (G-I). (A, D and G) The dominant docking result for non-ionizing EA (A), C4-OH-ionizing EA (D) and C-3-OH-ionizing EA (G) inside the peroxidase active site of COX I. The protein structure is shown in a flat ribbon format. In P+FeIV, carbon is colored in orange, nitrogen in blue, oxygen in red, hydrogen in white, and iron in navy blue. In EA, carbon is colored in green, oxygen in red, and hydrogen in white. (B, E and H) The same structure as in respective panels (A, D and G) with a white dash line added to indicate the distance between Fe4+ ion and O in one of EA's OHs. (C, F and I) Suggested potential hydrogen bonds (green dash lines) between the amino acid residues and the non-ionizing EA (C), C-4-OH-ionizing EA (F), and C-3-OH-ionizing EA (I). The amino acid residues are colored in light blue. EA, ellagic acid; COX I and COX II, cyclooxygenase I and II, respectively.