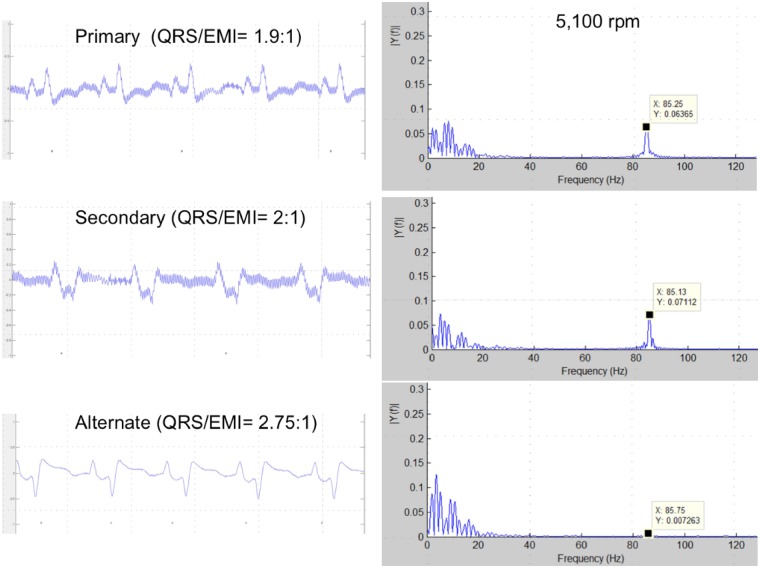
Figure 3.
Left: high-resolution capture displaying electromagnetic interference in the electrograms recorded from the three vectors. The ratio QRS/electromagnetic interference amplitude is higher in the alternate vector, making electromagnetic interference detection less likely. Right: frequency distribution of the same signals in a Fast-Fourier transform plot. Cardiac signal fundamental frequency and its harmonics are in the 0–20 Hz range. Plots displaying the distribution of detected frequencies in primary and secondary vectors show also a peak of frequency around 85 Hz generated by pump activity at 5100 rpm, detectable despite band-pass filter. In the alternate vector plot, an 85 Hz peak frequency is also present, but with lower amplitude.