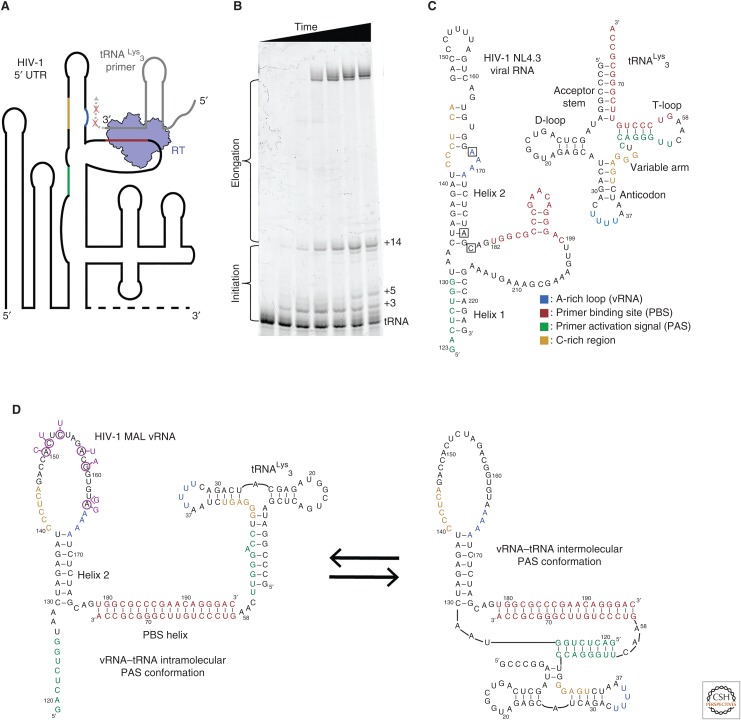
Figure 3.
(A) Reverse transcriptase (RT) must bind an 18-base-pair helix formed between the tRNA primer and the 5′ untranslated region (UTR) of the viral RNA genome (vRNA). The primer-binding site (PBS) helix resides in a highly structured region of the vRNA genome. RT has a rapid dissociation rate from the PBS helix and shows discrete pausing events during initiation (red ×s). (B) A primer extension gel in which polymerase extension reactions of RT for the vRNA–tRNA complex have been quenched at different time points. Unextended tRNA runs at the bottom of the gel and fully extended primer runs near the top. The buildup of pausing products can be seen in the lower half of the gel. (C) Secondary structures of the tRNALys3 primer and the NL4.3 human immunodeficiency virus 1 (HIV-1) subtype genome PBS region vRNA. Regions of sequence complementarity have been colored. Nucleotide positions that correspond to the pausing points seen in B are boxed on the vRNA. (D) NMR-derived structures of the MAL HIV-1 subtype genome in complex with the tRNA primer. Complementary sequences are colored as in C. Nucleotide mutations in MAL compared with NL4.3 are indicated in purple.