Figure 4.
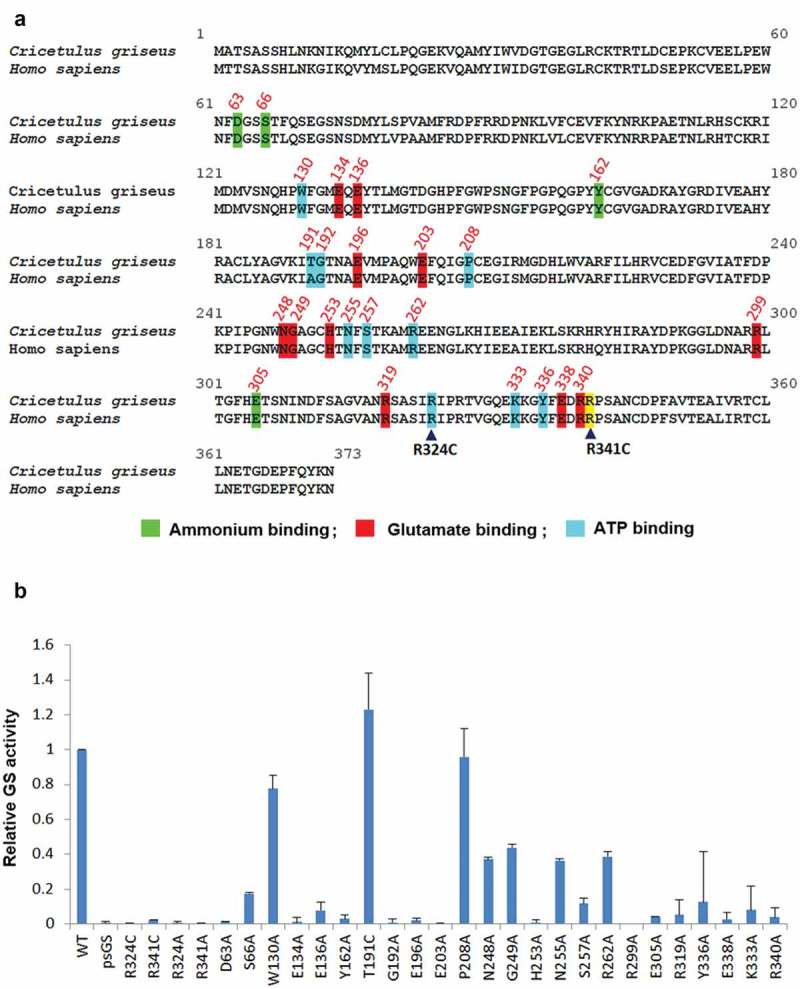
Identification of novel GS residues critical to GS activity. (a) Alignment of human and Chinese hamster GS protein sequences. Conserved sites involved in ammonium, glutamate and ATP binding are highlighted in green, red and blue as depicted together with their residue number.27 The congenital disease mutations R324C and R341C are pointed out with the black arrowheads. R341C residue is not involved in neither the ammonium, glutamate nor ATP binding, and is highlighted in yellow. (b) Comparison of GSwt activity with the various alanine mutants of the conserved residues highlighted in (a). The GS activities were normalized to luciferase activity to minimize expression level variations. Each GS construct was linked to a luciferase gene via IRES in a bicistronic manner. CHO-GS−/- clone 1 cells were transiently transfected with the constructs and total cell lysates were harvested. The GS activities were evaluated using the standard GS activity assay whereby GS–catalyzed formation of γ -glutamylhydroxamate from glutamine and hydroxylamine was measured photometrically at 500 nm. The activities of the mutants were represented as fold-change to GSwt.
