Figure 1.
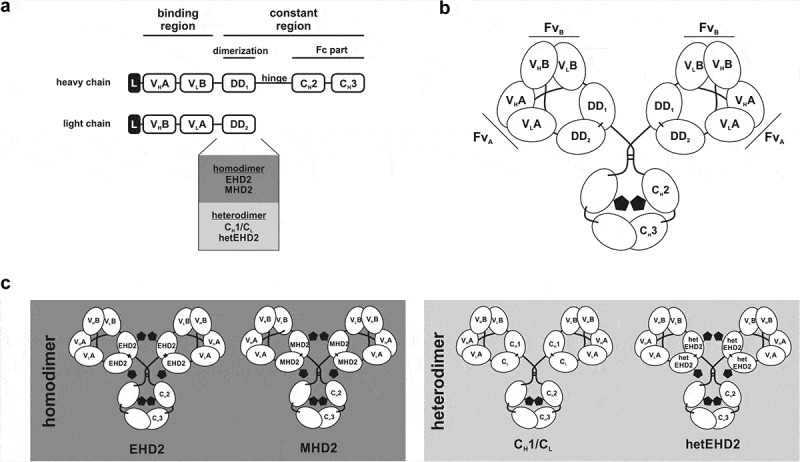
Tetravalent Db-Fc fusion proteins. (a) the schematic construction of a heavy and light chain of Db-Ig molecules. Variable domains are fused via G4S linker to build a diabody as binding region. The dimerization domain (DD1 and DD2) originate from either a heterodimer (CH1/CL or hetEHD2) or a homodimer (EHD2 or MHD2). The Fc part is formed by the hinge region and CH2/CH3 of an IgG. (b) schematic illustration of a tetravalent Db-Ig molecule with symmetric architecture. In dependence of the variable domains, this molecule can be either mono- (FvA = FvB) or bispecific (FvA≠FvB). N-glycans are shown as black pentagons. (c) Schematic illustration of tetravalent Db-Ig molecules using either homodimerization domains (EHD2 or MHD2) or heterodimerization domains (CH1/CL or hetEHD2). N-glycans are shown as black pentagons.
