Figure 1.
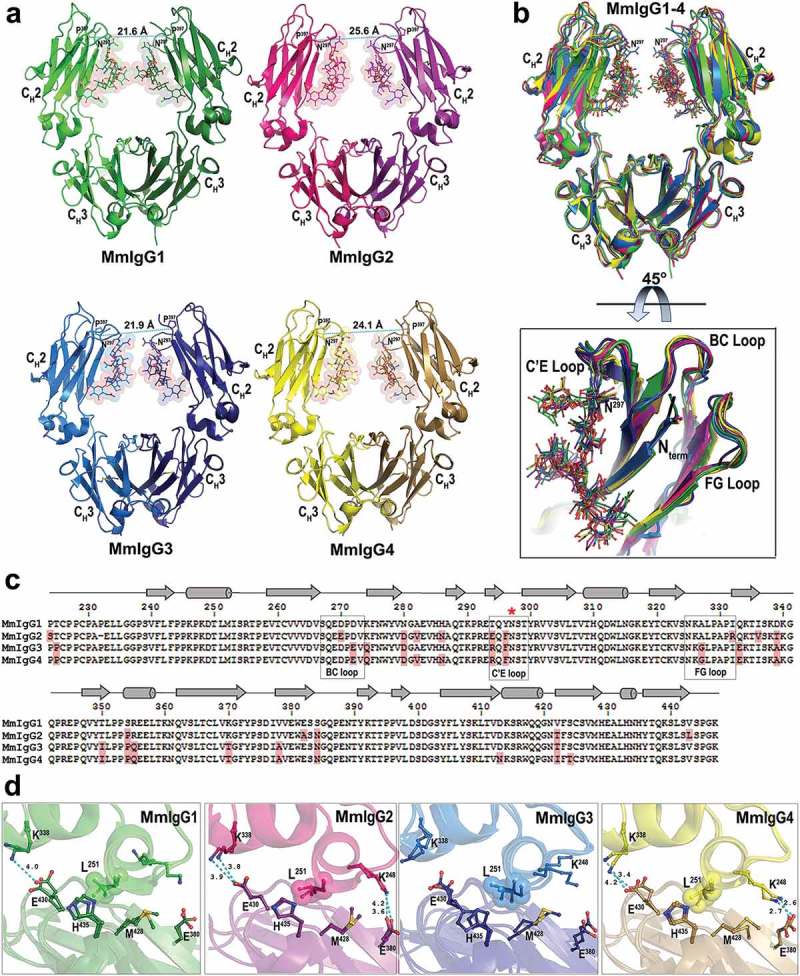
Crystal structures of the Rhesus macaque IgG1-4 Fc. (a) The overall structures are shown in a ribbon diagram with the two heavy chains (CH2-CH3 domains) in lighter and darker shades of green (MmIgG1), pink (MmIgG2), blue (MmIgG3) and yellow (MmIgG4). The sugars attached to N297 are shown as spheres colored by atom type (backbone color for carbon; red for oxygen and blue for nitrogen). The distances between Cα carbons of P238 are shown to indicate the differences in the distances between CH2 domains. (b) The structures of MmIgG1-4 Fcs were superimposed based on CH3-CH3 homodimer to show differences in the conformation and distances of CH2 domains in the Fc dimer. A 45° view shows the conformation of C’E, BC, and FG loops among CH2 domains of the Fcs. (c) Sequence alignment of the four subtypes of MmIgG Fc. The sequence identity among the four sequences is 86%. Residues of MmIgG2-4 different than MmIgG1 sequence are shaded in pink. The secondary elements as determined by the structures are shown above the sequence with arrows for β–strands, cylinders for α-helix and solid lines for random coil. Residue N297 is indicated with a red star and the C’E, BC, and FG loops are in boxes. (d) CH2−CH3 interface. Residues contributing to the interface through salt bridges/hydrogen bonds and residues of the hydrophobic “ball-in socket” joint are shown as sticks. Distances for hydrogen bonds/electrostatic interactions are as shown.
