Figure 5.
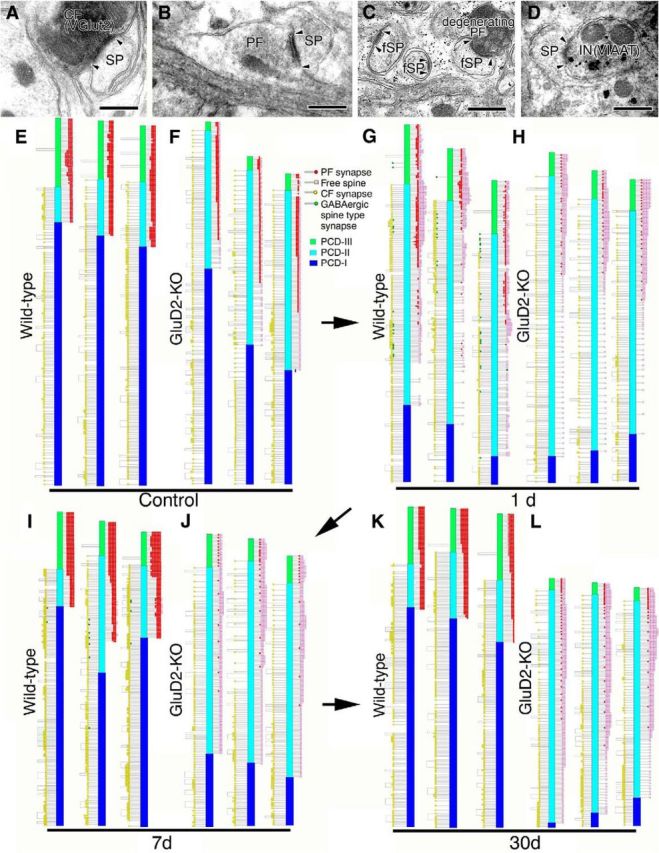
Ultrastructural reconstruction of dendritic innervation. A–D, Electron micrographs showing CF synapse labeled for VGluT2 by immunoperoxidase (A), PF synapse innervated by transverse axons on the transverse plane (B), free spines (fSP) and degenerating PF synapse 1 d after PF transection (C), and inhibitory synapse on PC spine labeled for VIAAT by silver-enhanced immunogold 1 d after PF transection (D). Compared with the well developed PSD in CF and PF synapses (pairs of arrowheads in A, B), the PSD in free spines is small and thin (pairs of arrowheads in C). E–L, Schematic illustrations showing the location of three kinds of spine-type synapses (PF synapse, red; CF synapse, yellow; inhibitory synapse, green) and free spines (pink) along reconstructed single dendritic tracts in sham-operated control (E, F) and PF-transected mice on postlesion days 1 (G, H), 7 (I, J), and 30 (K, L) in wild-type (E, G, I, K) and GluD2-KO (F, H, J, L) genotypes. We also illustrate the three distinct dendritic domains in different colors: PCD-I, blue; PCD-II, cyan; PCD-III, green. Scale bars, 500 nm.
