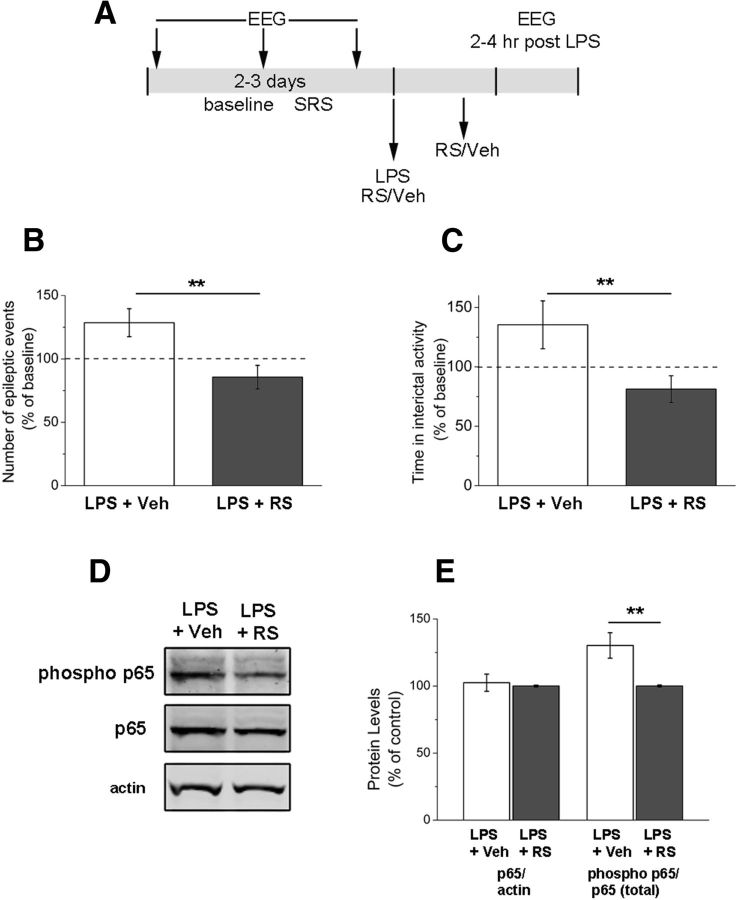
Figure 9.
Systemic delivery of a CCR2 receptor antagonist prevents the LPS-induced enhancement of epileptic activity. A, Experimental protocol. B, Frequency of epileptiform discharges (normalized to the baseline period) in animals treated with vehicle (veh) or RS102895 (RS), 2–4 h after LPS challenge. RS102895 prevents the enhancement of epileptic activity (t test, p < 0.01). C, Total time spent in interictal activity (normalized to the baseline period) in LPS-injected animals treated with vehicle or RS102895. CCR2 antagonism prevents the LPS-induced increase in interictal discharges (t test, p = 0.01). D, Immunoblotting showing the levels of total p65, phosphorylated (phospho) p65, and β-actin (loading control) in the sclerotic hippocampus of a representative LPS+vehicle (veh) and LPS+RS102895 (RS) mouse. E, Quantification of the immunoblotting data. The statistical analysis (t test, p = 0.01) indicates consistent reduction of the fraction of phosphorylated p65 in LPS+RS102895 (RS) mice compared with LPS+vehicle (veh). **p ≤ 0.01.