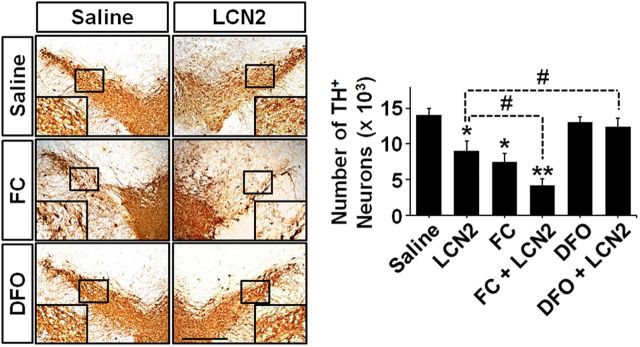
Figure 4.
Iron uptake upregulation enhances LCN2-mediated neurotoxicity in the SN. To clarify whether the function of LCN2 as an iron transporter contributes to neurotoxicity in the SN, we injected LCN2, FC, DFO, a mixture of LCN2 and FC, or a mixture of LCN2 and DFO into the SN and measured neurotoxicity by TH immunostaining 6 d after each treatment. Scale bar, 500 μm. Similar to the neurotoxicity in the SN shown in Figure 3, LCN2 treatment induced a significant decrease in the number of TH-positive neurons. In addition, FC alone also induced a loss of DA neurons in the SN and its neurotoxicity was enhanced significantly by cotreatment with FC and LCN2. However, LCN2-induced neurotoxicity was attenuated significantly by cotreatment with LCN2 and DFO, which showed no neurotoxicity on their own. *p < 0.01 and **p < 0.001 versus saline-treated mice; #p < 0.05 between the indicated group (one-way ANOVA; n = 5 for each group).