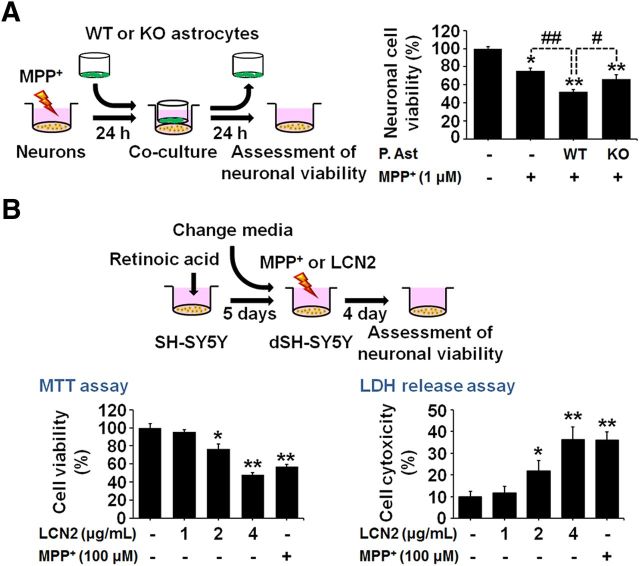
Figure 8.
LCN2 contributes to neurotoxicity in the MPP+-treated model of PD in vitro. A, Astrocytes isolated from WT or LCN2-deficient mice were cocultured with mesencephalic neurons treated with MPP+ for 24 h. Neuronal viability was measured using the MTT assay after 24 h of coculture. MPP+ induced significant neurotoxicity at 48 h after the treatment in mesencephalic-neuron-enriched cultures and the neurotoxicity was increased significantly in the cocultures with WT astrocytes. However, the addition of LCN2-deficient astrocytes induced lower neurotoxicity compared with cocultures of mesencephalic neurons and WT astrocytes. *p < 0.01 and **p < 0.001 versus untreated mesencephalic DA neurons; #p < 0.05 and ##p < 0.01 between the indicated groups. B, LCN2 treatment induces direct neurotoxicity in SH-SY5Y cultures. SH-SY5Y cells were differentiated by treatment with 10 μm RA for 5 d and then the cells were treated with LCN2 (1, 2, or 4 μg/ml) or MPP+ (100 μm) as a positive control for neurotoxicity. Cell viability was evaluated by MTT and LDH assays 4 d after the LCN2 or MPP+ treatment. *p < 0.05 and **p < 0.01, significantly different from untreated control (one-way ANOVA; n = 3).