Figure 1.
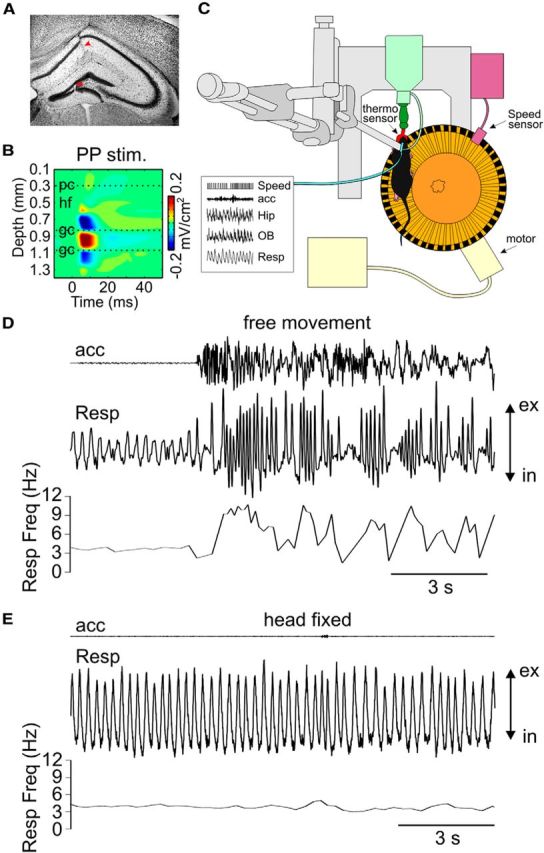
Simultaneous recording of motion, nasal respiration, and LFPs from the hippocampus and OB in awake mice. A, Localization of a multichannel probe inserted across the CA1-DG axis verified by histology (red arrowheads). B, Current source density analysis of LFPs in response to stimulation of perforant pathway (PP stim) used to identify anatomical landmarks. pc, Pyramidal cell layer; hf, hippocampal fissure; gc, granular cell layer. C, Setup for head-fixed experiments over a circular treadmill. An external thermocouple in front of the animal's nose records respiration. Speed is recorded during voluntary or forced running. Hip, Hippocampus; OB, olfactory bulb. D, Recordings of motion (acc: accelerometer), nasal respiration (Resp), and instantaneous frequency of respiration (Resp Freq) reveal high variability of respiration rate during free movement in the home cage. E, Stationary respiration rate during head-fixed experiments. ex, Expiration; in, inspiration.
