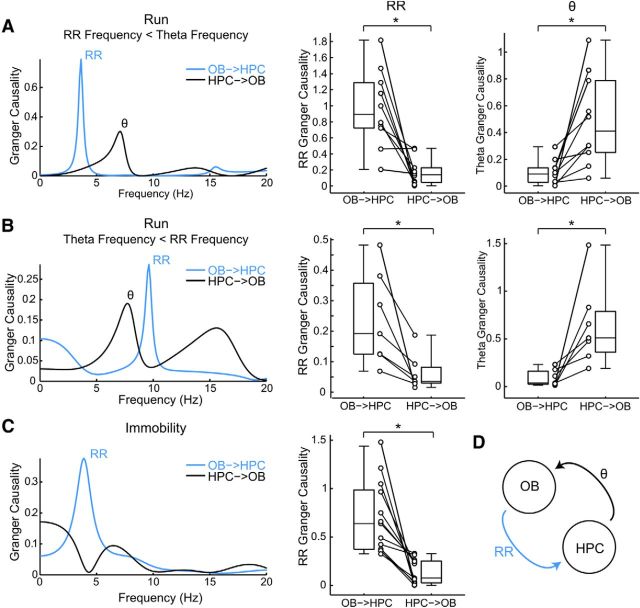
Figure 11.
Directionality analysis reveals that the OB causes the RR in the hippocampus, whereas the hippocampus causes theta (θ) in OB. A, B, Left, Examples of Granger causality spectra for LFPs recorded in OB and hippocampus (HPC) during treadmill running in which RR was slower (A) or faster (B) than theta (A: n = 10, *p < 0.005 for either comparison; B: n = 7, *p < 0.05 for either comparison; Wilcoxon signed rank test). Notice in both cases a peak in OB → HPC causality at RR frequency and a peak in HPC → OB causality at theta frequency. Boxplots on right represent group results. C, Same as above but for LFP recordings during head-fixed immobility (n = 13, *p < 0.0005; Wilcoxon signed rank test; theta causality was not analyzed because not all animals exhibited theta during immobility). D, Schematic depiction of RR and theta causal influences between OB and HPC.