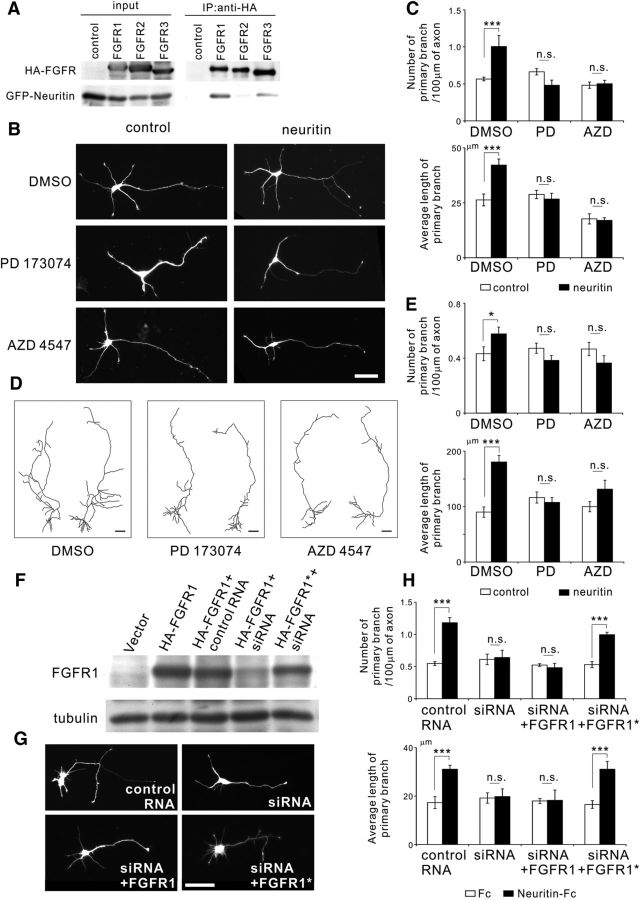
Figure 5.
Neuritin causes axonal branch formation in granule cells through the activation of FGFRs. A, Immunoprecipitation analysis showed the interaction between neuritin and FGFR1. The 293T cells expressing HA-tagged FGFR and GFP-tagged neuritin were lysed, and subsequent immunoprecipitation of the lysates was performed with anti-HA antibody. FGFR1 showed an interaction with neuritin. B, PD173074 (50 nm) or AZD4547 (100 nm), FGFR inhibitors, was applied to rat granule neurons expressing EGFP or expressing EGFP and neuritin at DIV 1. Neurons were fixed and imaged at DIV 4. Representative neurons are shown. Scale bar, 50 μm. C, Quantification of the number of primary branches per 100 μm of axon (DMSO: p < 0.001; PD173074: p = 0.065; and AZD4547: p = 0.751) and the average length of primary branches (DMSO: p < 0.001; PD173074: p = 0.621; and AZD4547: p = 0.843) from three or four independent experiments; n = 30 for each. ***p < 0.005 (one-way ANOVA for each reagent). n.s., Not significant. D, Reconstructions of EGFP-expressing neurons or EGFP and neuritin-expressing neurons in rat hippocampal slice cultures. PD 173074 (100 nm) or AZD4547 (200 nm) was administered from DIV 8 to DIV 11, and slices were fixed at DIV 11. Scale bar, 50 μm. E, Quantification of the number of primary branches per 100 μm of axon (DMSO: p = 0.034; PD173074: p = 0.116; and AZD4547: p = 0.198) and the average length of primary branches (DMSO: p < 0.001; PD173074: p = 0.526; and AZD4547: p = 0.140); n = 19–21 total for each; the data were collected from three to five independent experiments. *p < 0.05 (one-way ANOVA for each reagent). ***p < 0.005 (one-way ANOVA for each reagent). n.s., Not significant. F, Validation of Stealth RNAi against rat FGFR1. The 293T cells were transfected with control RNA or Stealth RNAi against rat FGFR1 and a mock vector, HA-FGFR1, or HA-FGFR1* (RNAi resistant mutant), as indicated in the figure. Cells were lysed 36 h later, and immunoblotting was performed with anti-HA and anti-tubulin antibody. G, Knockdown of FGFR1 expression suppressed neuritin-dependent axonal branching. Rat granule neurons were transfected with EGFP-expressing plasmids, control RNA or Stealth RNAi against rat FGFR1, and FGFR1 or FGFR1*-expressing plasmids before being plated. Fc or Neuritin-Fc (1 μg/ml) was administered at DIV 1, and neurons were fixed at DIV 4. Representative neurons with Neuritin-Fc are shown. Scale bar, 50 μm. H, Quantification of the number of primary branches per 100 μm of axon (control RNA: p < 0.001; RNAi: p = 0.787; RNAi+FGFR1: p = 0.650; and RNAi+FGFR1*: p < 0.001) and the average length of primary branches (control RNA: p < 0.001; RNAi: p = 0.846; RNAi+FGFR1: p = 0.941; and RNAi+FGFR1*: p < 0.001) from three independent experiments with n = 30 for each. ***p < 0.005 (one-way ANOVA for each set of nucleotides). n.s., Not significant.