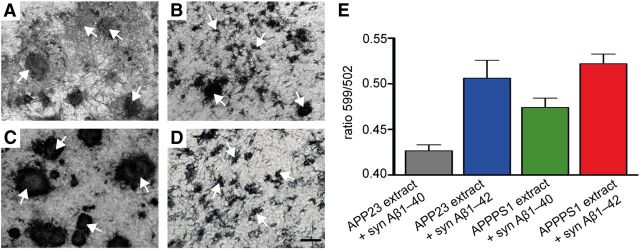
Figure 3.
Aβ morphotypes in HSCs depend on the seed and synthetic Aβ species. A–D, Differences in structural appearance of induced Aβ deposits (anti-Aβ immunostaining) in 10-week-old wild-type HSCs inoculated with different brain extracts and incubated with 1.5 μm of either synthetic (syn) Aβ1–40 or Aβ1–42 in the culture medium. A, Large fibrillary deposits of Aβ (arrows) were observed with APP23 brain extract and syn Aβ1–40. B, Inoculation with APP23 brain extract and syn Aβ1–42 revealed a mixed pattern of small and large fibrillary deposits. C, APPPS1 brain extract combined with syn Aβ1–40 revealed large and compact Aβ deposits, whereas (D) numerous small Aβ deposits (arrows) were seen with APPPS1 brain extract and syn Aβ1–42. Scale bars: A–D, 20 μm. E, Spectral properties of the induced Aβ deposits using the conformation-dependent amyloid-specific dye pFTAA. For quantitative comparison, the ratio of light emitted at 599 and 502 nm was assessed for individual Aβ deposits and the mean ratio determined per HSC. Per condition, 11–13 HSCs were analyzed; data are mean ± SEM. ANOVA (extract × syn Aβ) revealed a significant effect for extract (F(1,43) = 6.41; p < 0.05) and syn Aβ (F(1,43) = 26.17; p < 0.001) but failed to reach significance for the interaction (F(1,43) = 1.61; p > 0.05).