Figure 1.
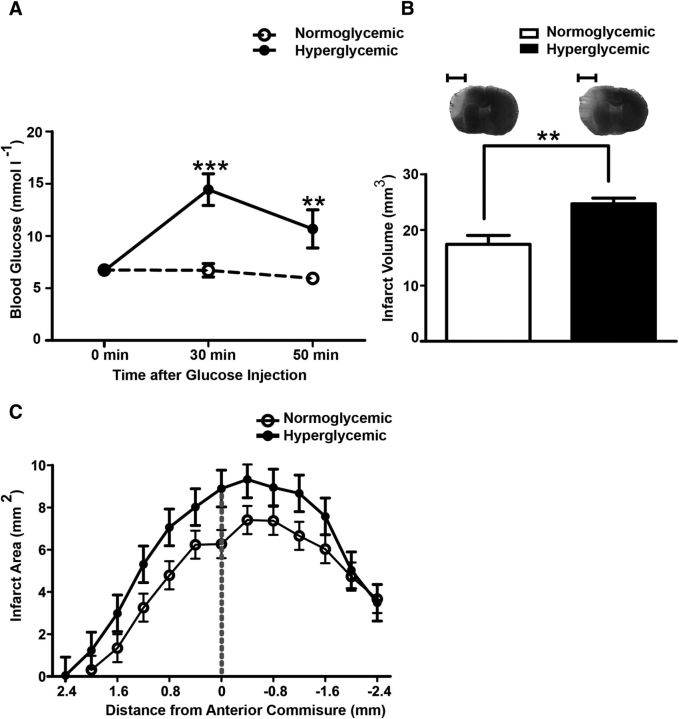
Hyperglycemia increases the infarct volume. A, Blood glucose concentrations were significantly increased when mice were treated with 50 mg of glucose. Blood glucose concentrations were measured in anesthetized mice immediately before (0 min) and 30 min and 50 min after the glucose or normal saline injections. MCAO was performed after the first measurement. Two-way ANOVA, for glucose F(1, 36) = 12.52, p = 0.0023. ***p ≤ 0.001. **p ≤ 0.01 (Bonferroni posttests, n = 11 mice/group). B, Forty-eight hours after MCAO, the hyperglycemic group had larger infarcts than the normoglycemic group. Typical silver-stained coronal brain sections showing infarcts in light gray are depicted on top of the panel. Unpaired t test, **p < 0.001 (n = 13 mice/group). Scale bar, 2.5 mm. C, Distribution of infarcts on coronal sections in normoglycemic and hyperglycemic groups (F(1,240) = 13.9, p = 0.0013, repeated-measures ANOVA, n = 11 mice/group). Data are shown as means ± SEM.