Figure 1.
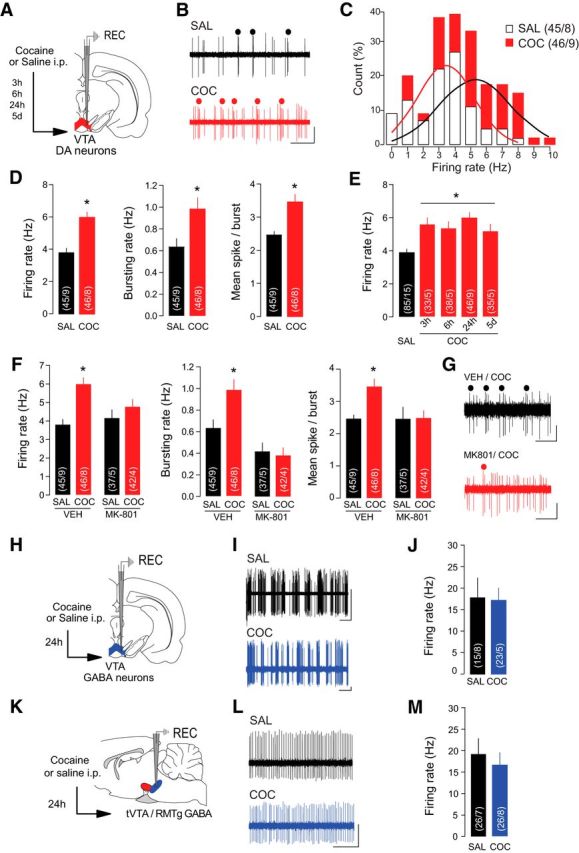
Cocaine increases firing rate and burst firing of VTA DA neurons in vivo. A, Schematic of the experimental design. Rats received an injection of cocaine (COC) or saline (SAL) 24 h before recordings of VTA DA neurons except where indicated (E). B, Representative traces from VTA DA neurons with burst events indicated. Scale bars: horizontal, 1 s; vertical, 1 mV. C, Distribution of VTA DA neurons by their firing rate. Solid line represents the best-fit normal distribution curve for the histogram data. D, Firing rate (left), bursting rate (middle), and mean spikes per burst (right) of VTA DA neurons were increased in COC-treated rats. E, The increase in VTA DA firing rate was significant when recordings were performed 3 h, 6 h, 24 h, and 5 d after COC exposure. F, Pretreatment with NMDAR antagonist MK-801 occluded COC-induced increases in firing rate (left), bursting rate (middle), and mean spikes per burst (right) of VTA DA neurons. G, Representative traces of VTA DA neurons from COC-treated rats with or without MK-801 pretreatment. Scale bars: horizontal, 1 s; vertical, 0.5 mV. H, Schematic of the experimental design. Rats were treated with SAL or COC 24 h before recording putative VTA GABA neurons. I, Sample traces from putative VTA GABA neurons. Scale bars: horizontal, 2 s; vertical, 0.5 mV. J, Firing rate of VTA GABA neurons was not altered by COC. K, Schematic of the experimental design. Rats were treated with SAL or COC 24 h before recording GABA neurons in the tVTA/RMTg. L, Sample traces from GABA tVTA/RMTg neurons. Scale bars: horizontal, 0.5 s; vertical, 1 mV. M, Firing rate of tVTA/RMTg GABA neurons was not altered by COC. *p < 0.05.
