Figure 1.
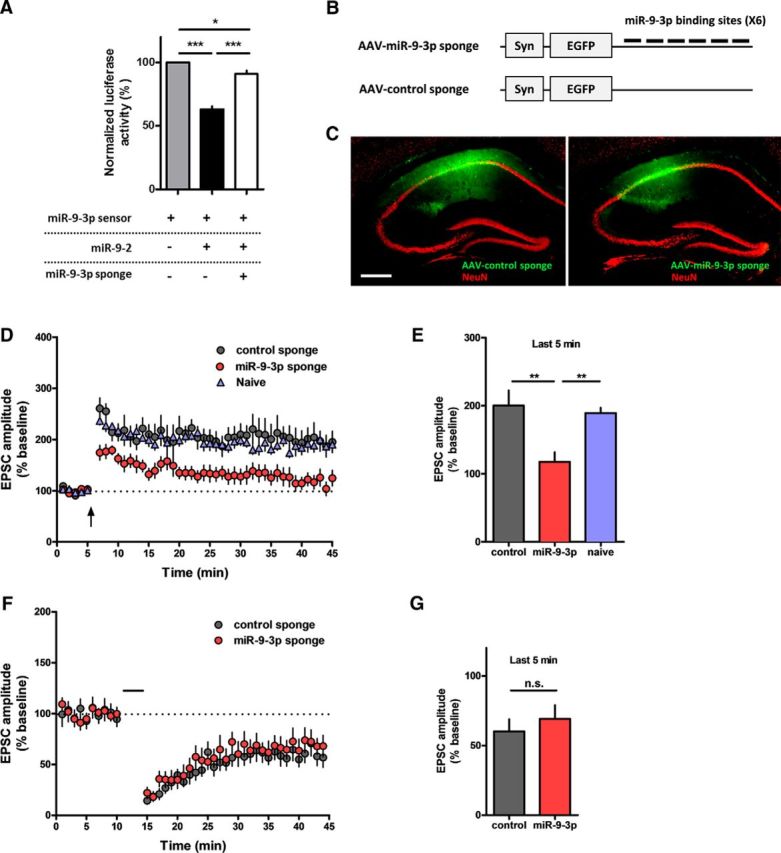
AAV-miR-9-3p sponge-mediated miR-9-3p inhibition blocks hippocampal LTP. A, Luciferase assay showing that the miR-9-3p sponge specifically suppresses the activity of miR-9-3p (*p < 0.05, ***p < 0.001, n = 5 per group, Tukey's multiple-comparisons test after significant 1-way ANOVA). The expression of miR-9-2, a genetic locus encoding miR-9-5p/3p, inhibited the expression of the miR-9-3p sensor, which rescued by cotransfection of the miR-9-3p sponge. B, Schematic diagrams of AAV-miR-9-3p-sponge. Six bulged miR-9-3p-binding sites were contained in the 3′ UTR of the EGFP gene. C, Representative fluorescence images showing EGFP expression in hippocampus 4 weeks after injection of AAV-miR-sponge. Scale bar, 300 μm. D, Theta-burst LTP recordings were significantly impaired in miR-9-3p sponge-expressing neurons. E, Summary graph representing the average EPSC amplitudes of the last 5 min of recording in naive, control sponge, and miR-9-3p sponge groups (last 5 min of recording, control, n = 6 cells from 3 mice, miR-9-3p, n = 9 cells from 6 mice, naive, n = 7 cells from 5 mice, **p < 0.01, Tukey's multiple-comparisons test after 1-way ANOVA). F, Hippocampal LTD was comparable between control and miR-9-5p sponge-expressing neurons. G, Summary graph representing the average EPSC amplitudes of the last 5 min recording in control sponge and miR-9-3p sponge groups (last 5 min of recording, control, n = 9 cells from 4 mice, miR-9-3p, n = 7 cells from 3 mice, unpaired two-tailed t test, t(14) = 0.6813, p = 0.5068). Data are mean ± SEM.
