Figure 1.
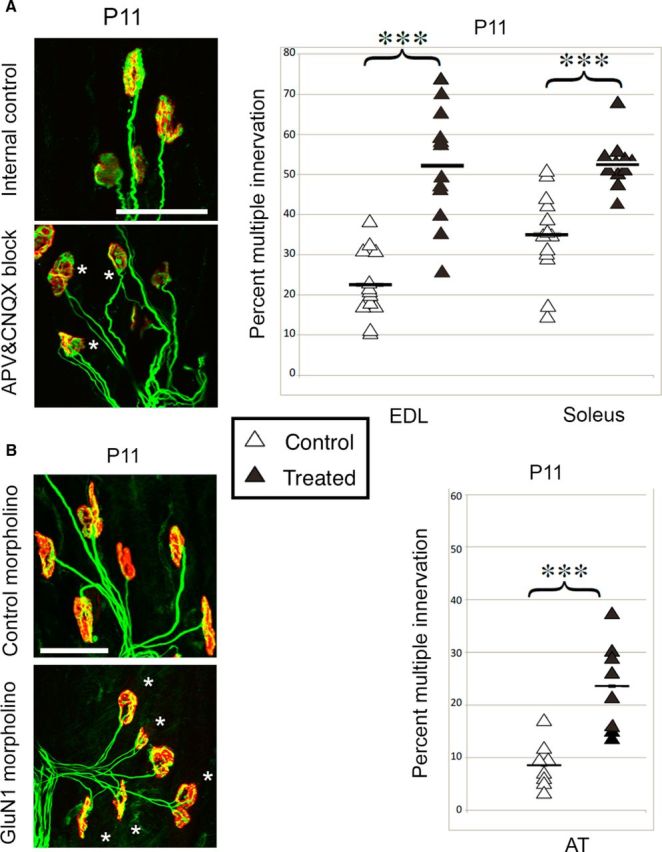
Reduction of NMDA receptor activity slows synapse elimination. A, Pharmacological reduction of NMDA and AMPA receptor activity with AP5 and CNQX between P4 and P11. Left, Whole-mount NMJ immunolabeling in anterior tibialis (AT) muscle of P11 pups. Asterisks show polyinnervated end plates. Red, Rhodamine-α-bungarotoxin labels ACh receptors. Green, Antibodies SV2 and 2H3 label synaptic vesicles and neurofilaments. Right, Means and distributions of percentage of multiply innervated muscles. Open symbols indicate control; filled symbols, treated; horizontal lines, means. The treated muscles contained significantly more multiply innervated fibers than the contralateral internal control muscles (EDL: 22 ± 3% control limb vs 52 ± 4% treated limb, p = 0.00006, n = 12, 12; soleus: 35 ± 3% control limb vs 53 ± 2% treated limb, p = 0.00001, n = 11, 13). B, Vivo-morpholino downregulation of GluN1 expression between P4 and P11. A vivo-morpholino was pressure injected into the AT muscle end plate band in P4 pups. Conventions are as in A. The AT muscle demonstrated significant retention (9 ± 5% internal control limb vs 24 ± 8% treated limb, p = 0.001, n = 8, 8). Scale bars, 50 μm.
