Figure 4.
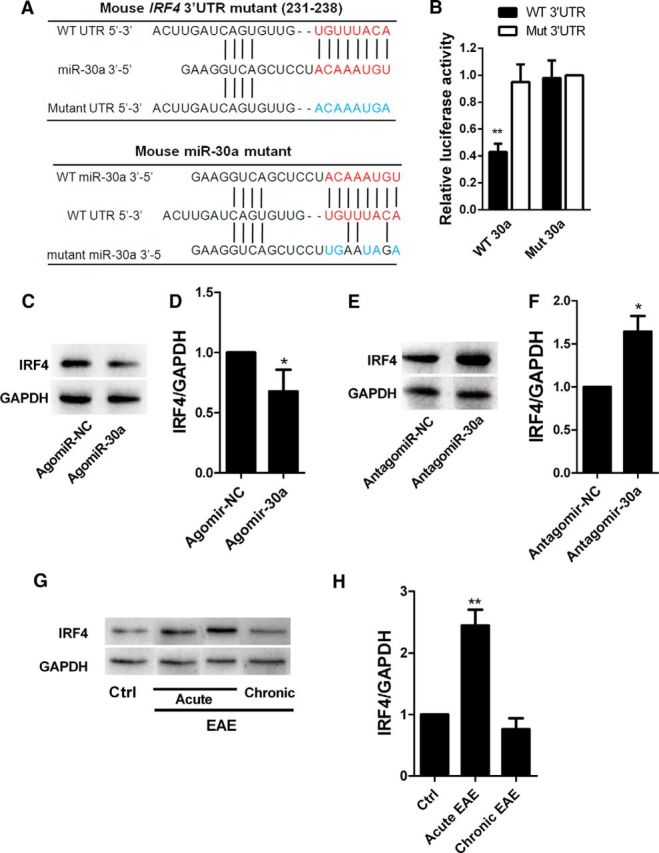
IRF4 is the functional target of miR-30a. A, Putative miR-30a-binding sites in IRF4 mRNA 3′-UTR and mutations in the IRF4 mRNA 3′-UTR (top) and miR-30a (bottom). B, Luciferase activity of reporter carrying the mutated (Mut3′-UTR) or wild-type (WT3′-UTR) IRF4 mRNA 3′-UTR cotransfected into HEK293T cells with wild-type miR-30a (WT 30a) or its mutant (mutant 30a) (n = 3 independent experiments). C, Western blot analysis of IRF4 in CD4+ T cells after transduction with AgomiR-30a or its control (Agomir-NC) for 6 d. D, Quantification of IRF4 densitometry normalized to GAPDH in C (n = 3 independent experiments). E, Western blot analysis of IRF4 in CD4+ T cells after transduction with AntagomiR-30a or its control (Antagomir-NC) for 6 d. F, Quantification of IRF4 densitometry normalized to GAPDH in E (n = 3 independent experiments). G, Western blot analysis of IRF4 in CD4+ T cells from EAE mice at different phases. H, Quantification of IRF4 densitometry normalized to GAPDH in G (n = 3 independent experiments; *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001 vs control; D, F, Student's t test; B, H, one-way ANOVA with Dunnett's post hoc test). Data are from at least three experiments and are shown as mean ± SEM.
