Figure 1.
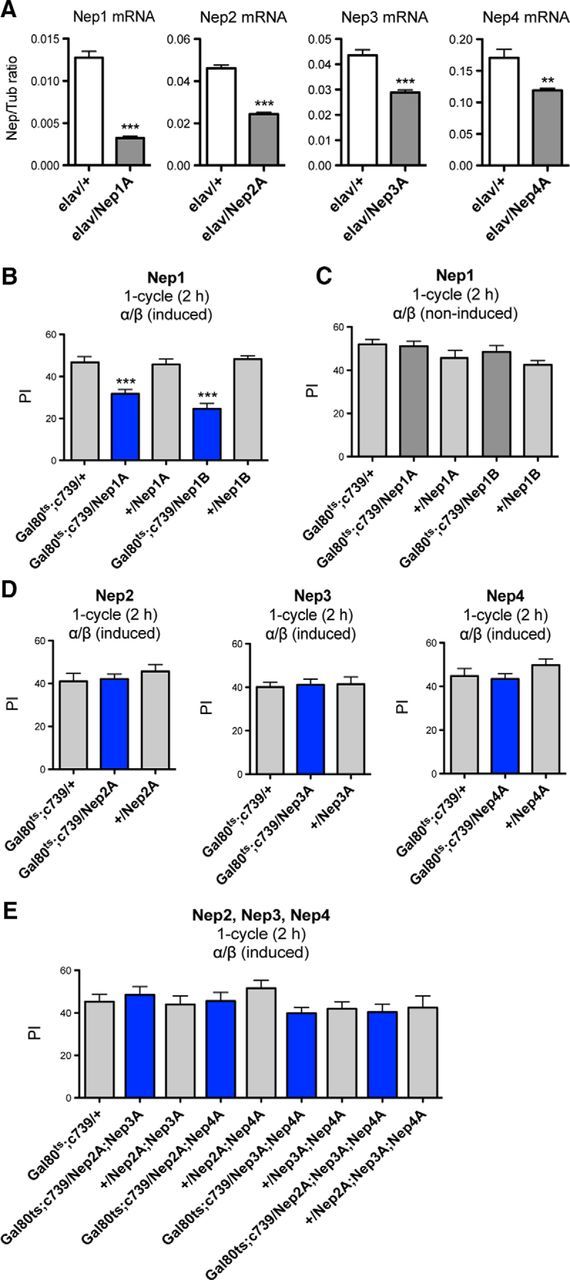
Nep1 inhibition in the adult α/β MB neurons induces a MTM deficit. A, Neprilysin mRNA is targeted efficiently by RNAi-Nep constructs. Shown are qPCR analyses of neprilysin expression. Total RNA was extracted from elav/+ and elav/RNAi-Nep fly heads and further reverse transcribed with olig(dT) primers. Resulting cDNA was quantified using tubulin (Tub) expression as a reference. Results are shown as ratios to the reference (Nep1: t test, ***p < 0.0001, n = 4; Nep2: t test, ***p < 0.0001, n = 6; Nep3: t test, ***p = 0.0008, n = 4; Nep4: t test, **p = 0.0094, n = 4). B, C, Nep1 expression in adult α/β MB neurons is involved in MTM. B, After 3 d of induction, Gal80ts;c739/Nep1A and /Nep1B flies exhibit MTM deficits (F(4,45) = 20.98, p < 0.0001, n ≥ 8; post hoc Newman–Keuls test, Gal80ts;c739/Nep1A vs Gal80ts;c739/+ ***p < 0.001, Gal80ts;c739/Nep1A vs +/Nep1A ***p < 0.001, Gal80ts;c739/Nep1B vs Gal80ts;c739/+ ***p < 0.001, Gal80ts;c739/Nep1B vs +/Nep1B ***p < 0.001). C, In the absence of Gal4 induction, Gal80ts;c739/Nep1A and /Nep1B flies exhibit similar MTM scores to their respective genetic controls (F(4,64) = 2.039, p = 0.1003, n ≥ 11). D, E, Nep2, Nep3, and Nep4 silencing in adult α/β MB neurons does not alter MTM. D, Single Nep knock-down MTM analyses with the Gal80ts;c739 driver. RNAi-expressing flies show similar MTM scores to the genetic controls (Nep2A: F(2,26) = 0.5832, p = 0.5658, n = 9; Nep3A: F(2,26) = 0.06404, p = 0.9381, n = 9; Nep4A: F(2,25) = 1.233, p = 0.3100, n ≥ 8). E, Analyses of double and triple Nep knock-down with the Gal80ts;c739 driver. RNAi-expressing flies show similar MTM scores to their genetic controls (F(6,106) = 1.250, p = 0.2874, n ≥ 10). Error bars indicate mean ± SEM. PI, Performance index.
