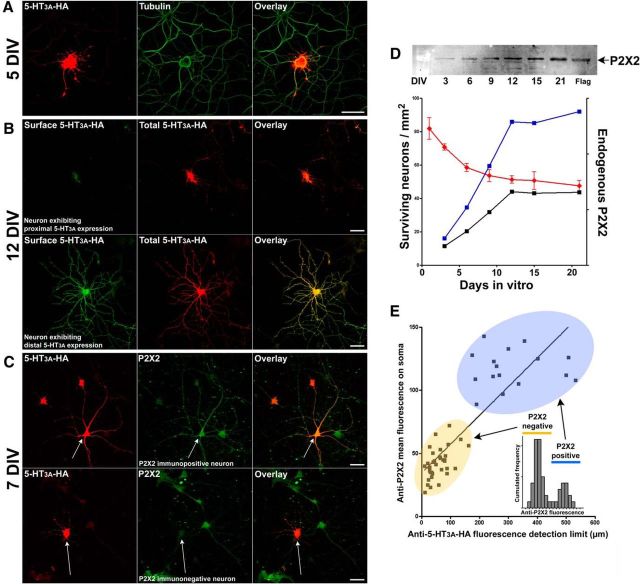
Figure 3.
5-HT3A receptor distal targeting is dependent on endogenous P2X2 receptors. Hippocampal neurons were transfected at (A) 5 DIV, (B) 12 DIV, or (C) 7 DIV, with 5-HT3AR-HA. Immunofluorescence detection was performed with the following: A, anti-HA (red) and anti-tubulin (green) antibodies; B, anti-HA antibodies without permeabilization (green), and then anti-HA antibodies after permeabilization (red); or C, anti-HA (red) and anti-P2X2 (green) antibodies. Scale bars, 50 μm. D, Endogenous P2X2R (arbitrary units) were quantified by Western blot (black line) in hippocampal cultures at the indicated times (DIV). Surviving neurons were counted for each condition (red line), and the amount of endogenous P2X2R was divided by the number of live neurons in the culture at each time (blue line, endogenous P2X2/surviving neurons). E, The intensity of mean endogenous anti-P2X2R immunofluorescence (arbitrary units) measured on neuron somas was plotted versus the distance of the 5-HT3A-HA detection limit (above background) along the longest immunolabeled neurite at 7 DIV (C). The cumulated frequency distribution of P2X2R mean fluorescence intensity on somas (inset) revealed the existence of two populations of neurons (n = 51, bimodal distribution, median = 50): P2X2 immunonegative (68.3%, μ1 = 47, quartiles = 40) and P2X2 immunopositive (31.6%, μ2 = 121, quartiles = 110). Only P2X2R-immunopositive neurons (example in C) expressed 5-HT3AR distally (linear regression, r2 = 0.71, p < 0.0001).