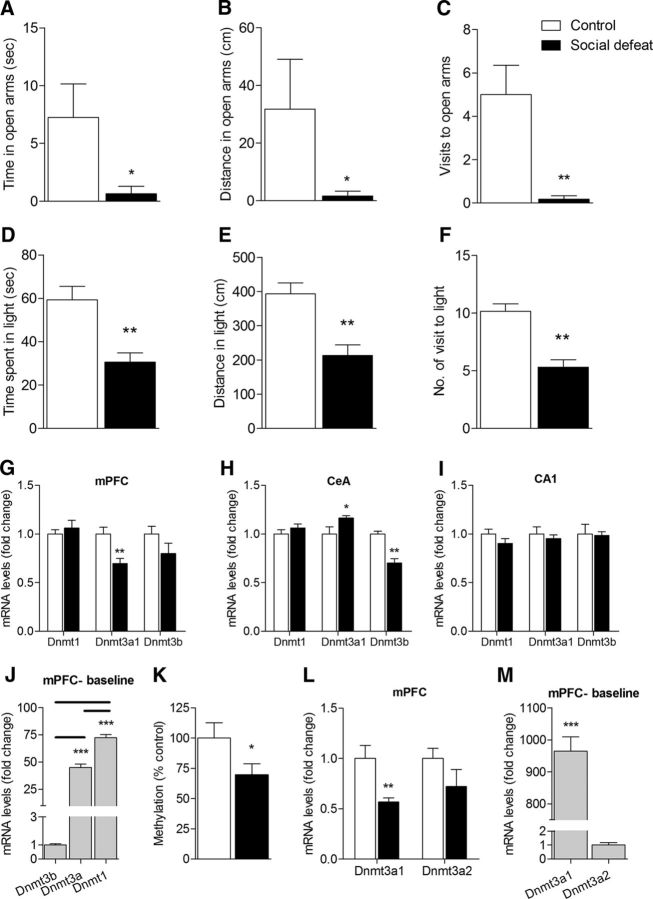
Figure 1.
A–F, Increase in anxiety-like behavior in mice subjected to CSDS as measured by the EPM and DLT tests. In the EPM test, CSDS mice showed (A) a significant reduction in the time spent in, (B) distance traveled, and (C) made significantly fewer visits to the open arms compared with control mice. n = 5 (Mann–Whitney U test). In the DLT test, CSDS mice showed a significant reduction in (D) time spent in, (E) distance traveled in, and (F) made fewer entries into the light compartment compared with controls. n = 13 or 14 (Students' t test). G–I, Transcriptional regulation of mPFC-Dnmt3a by CSDS. mRNA levels of Dnmt1, Dnmt3a, and Dnmt3b were determined in stress-related brain areas following the CSDS protocol, using qRT-PCR analysis. G, Dnmt3a mRNA levels were found to be significantly downregulated in the mPFC of CSDS mice compared with controls. H, Dnmt3a mRNA levels were significantly upregulated, whereas Dnmt3b mRNA levels were significantly downregulated in the central amygdala (CeA) of CSDS mice. I, No significant differences were found in Dnmts' transcripts in the CA1. n = 4–7 (Student's t test). J, Dnmt1 basal mRNA expression in the mPFC is significantly higher in comparison to Dnmt3a, which in turn is significantly higher in comparison to Dnmt3b. n = 13 (one-way ANOVA followed by Student's t test). K, Global DNA methylation was significantly decreased in the mPFC 4 weeks following CSDS. L, M, Expression of Dnmt3a splice variants in the mPFC. L, mPFC-Dnmt3a1 mRNA levels are downregulated following CSDS, whereas Dnmt3a2 has no significant change. M, Dnmt3a1 basal mRNA levels in the mPFC are significantly higher compared with Dnmt3a2levels. n = 5–8 (Student's t test). *p < 0.05. **p < 0.01. *** p < 0.001. Data are mean ± SEM.