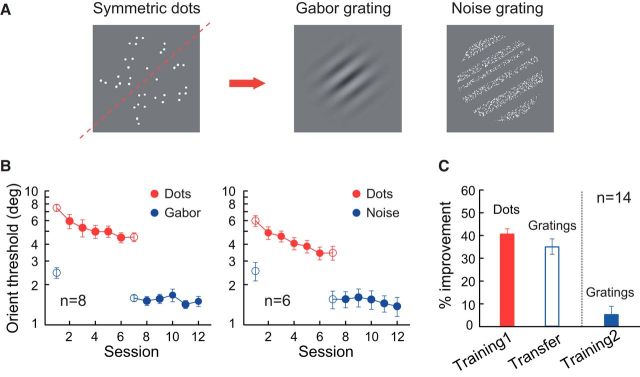
Figure 1.
Transfer of orientation discrimination learning from symmetric dot patterns to gratings. A, Sample stimuli. The symmetry axis is indicated by the red dashed line (not shown in the actual stimuli). The arrow indicates the direction of learning transfer. B, Session-by-session mean discrimination thresholds for dot pattern orientation (“Dots”) and grating orientation (“Gabor” or “Noise”). Grating orientation discrimination was tested with Gabor gratings (left) and noise gratings (right). C, Summary of dot pattern orientation learning and its transfer to grating orientation (“Training1” and “Transfer”; left two bars) and the impact of further grating orientation training (“Training2”; right bar). Data are averaged over the two panels in B. The percentage improvement was calculated as (pretraining threshold − posttraining threshold)/pretraining threshold. Error bars indicate ±SEM.