Figure 5: Loss of LKB1 confers sensitivity to dual inhibition of mTOR and PI3K by GSK2126458 in vivo.
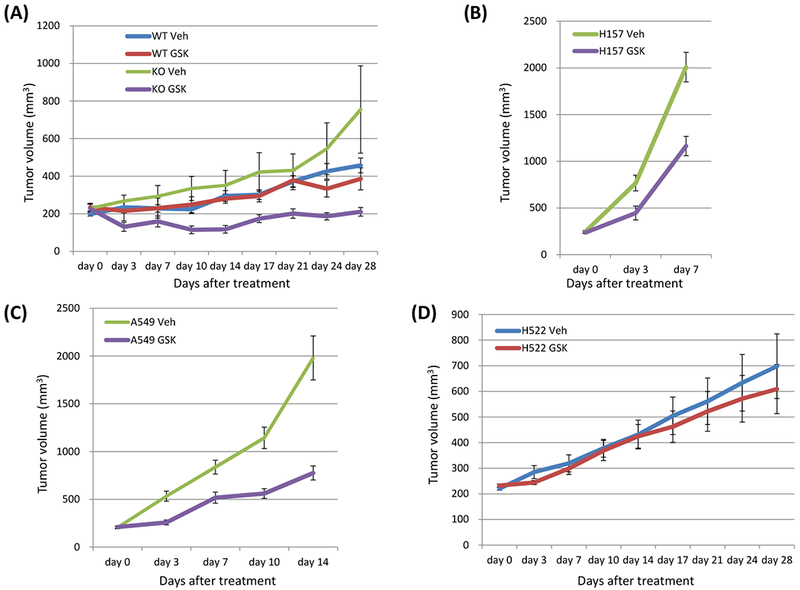
A, An LKB1 knock out clone and a wild type clone of H358 cells (5 × 106 cells) were inoculated into the flank of NSG mice, and when tumor volumes reached approximately 200 mm3, the mice were treated with GSK2126458 0.5 mg/kg/mouse or vehicle, p.o.. days 1-5, 8-12, 15-19, and 22-26. Data shown are mean ± SE for 7 to 9 mice in each group (7 mice injected LKB1 knock out clones and 8 mice injected LKB1 wild type clones were treated with GSK2126458, and 9 mice injected LKB1 knock out clones and 9 mice injected LKB1 wild type clones were treated with vehicle). Xenograft tumors of mice were evaluated as described in Materials and Method. Tumor size was analyzed by Wilcoxon rank sum test (KO veh vs. KO GSK day 0 p = 0.5251, day 3 p = 0.0018, day 7 p = 0.0502, day 10 p = 0.0036, day 14 p = 0.0050, day 17 p = 0.0528, day 21 p = 0.0389, day 24 p = 0.0117, day 28 p = 0.0163; WT GSK vs. KO GSK day 0 p = 1.0000, day 3 p = 0.1052, day 7 p = 0.2976, day 10 p = 0.0206, day 14 p = 0.0078, day 17 p = 0.0707, day 21 p = 0.0282, day 24 p = 0.0707, day 28 p = 0528). B, C, D Two LKB1 mutant cells (H157 and A549) and one LKB1 wild type cells (H522) were inoculated into the flank of NSG mice, and when tumor volumes reached approximately 200 mm3, the mice were treated with GSK2126458 0.5 mg/kg/mouse or vehicle, p.o.. days 1-5, 8-12, 15-19, and 22-26. Data shown are mean ± SE for 10 to 11 mice in each group (11 mice injected H157 were treated with vehicle, 11 injected H157 were treated with GSK2126458, 11 injected A549 were treated with vehicle, 11 injected A549 were treated with GSK2126458, 10 injected H522 were treated with vehicle, and 10 injected H522 were treated with GSK2126458). Xenograft tumors of mice were evaluated as described in Materials and Method. Tumor size was analyzed by Wilcoxon rank sum test (H157 veh vs. H157 GSK day 0 p = 0.4698, day 3 p = 0.0138, day 7 p = 0.0012; A549 veh vs. A549 GSK day 0 p = 0.7928, day 3 p = 0.0009, day 7 p = 0.0043, day 10 p = 0.0006, day 14 p = 0.0009; H522 veh vs. H522 GSK day 0 p = 0.1988, day 3 p = 0.1208, day 7 p = 0.8206, day 10 p = 0.6230, day 14 p = 0.9397, day 17 p = 0.4963, day 21 p = 0.5967, day 24 p = 0.4057, day 28 p = 0.5453). The H157 cells grew very rapidly and the majority of the vehicle treated mice (10 of 11) had to be euthanized because they met early removal criteria by day seven and the study was stopped. Although tumors in the treated mice grew slower, several of the mice (5 of 11) treated with GSK2126458 also had to be euthanized due to meeting early removal criteria at day seven. For the A549 cell line, at day 14, most of the vehicle treated mice (9 of 11) met early removal criteria while GSK2126458 treated mice (4 of 11) met early removal criteria at this time and the study was stopped. Abbreviations; WT; wild type, KO; knock out, Veh; vehicle, GSK; GSK2126458.
