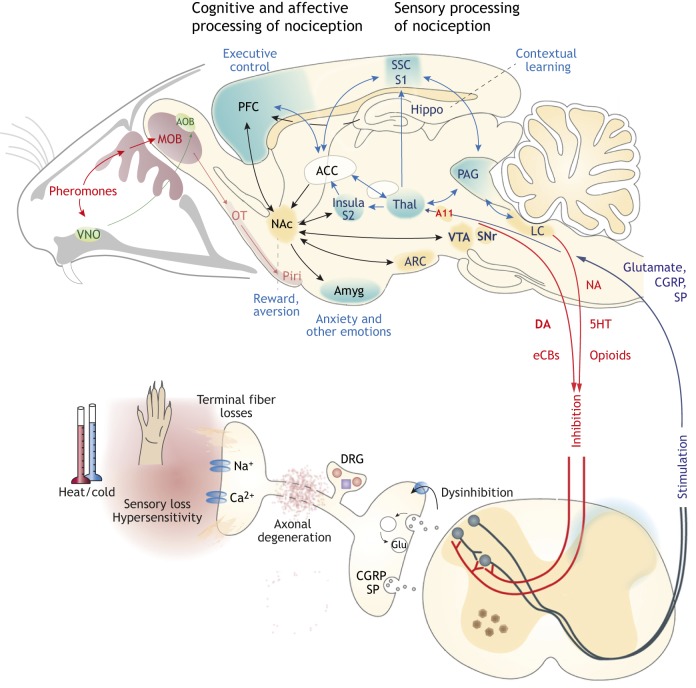
Fig. 2.
Nociception and olfaction in PD. Sensory processing of nociception involves primary nociceptive neurons in the dorsal root ganglia (DRG), secondary projection neurons in the dorsal horn of the spinal cord, the dorsolateral thalamus and somatosensory cortex (SSC, S1). This direct path connects to the prefrontal cortex (PFC), the insula cortex and the limbic system – amygdala (Amyg), anterior cingulate cortex (ACC), nucleus accumbens (NAc), areas of the midbrain [e.g. ventral tegmental area (VTA); periaqueductal gray (PAG)] and hippocampus. These areas process the cognitive and affective modulation of ‘pain’ and are needed to feel the reward associated with pain relief. This pain-relief reward is based on the release of DA in the NAc from VTA afferents and is strengthened by endocannabinoids. In addition, DAergic pain-inhibiting pathways arise from the midbrain and signal to the dorsal horn of the spinal cord. Although VTA neurons are less vulnerable to genetic causes or toxins than DA neurons of the substantia nigra, dysfunctions in these reward and pain-inhibitory pathways likely contribute to PD-associated pain. Sensory neurons are particularly vulnerable to defects of the ubiquitin-proteasome system (UPS), loss of mitochondria and inflammation, which result in axonal damage and loss of terminal nerve fiber endings. Clinically, fiber loss manifests as small-fiber or mixed-fiber sensory neuropathies, with sensory losses and pain. Rodent models of PD more or less recapitulate the sensory loss of smell, taste and nociception, which may precede motor-function deficits. Prodromal pain and olfactory deficits are highly prevalent, the latter resulting from degenerations of olfactory sensory neurons. SNCA deposits in the olfactory bulb spread to the projections to the olfactory cortex and areas involved in regulation of social behavior, nutrition and hormonal balances. AOB, accessory olfactory bulb; ARC, arcuate nucleus; CGRP, calcitonin-related peptide; eCBs, endocannabinoids; LC, locus coeruleus; MOB, main olfactory bulb; NA, noradrenaline; 5HT, serotonin; OT, olfactory tract; Piri, piriform cortex; SNr, substantia nigra; SP, substance P; Thal, thalamus; VNO, vomeronasal organ.